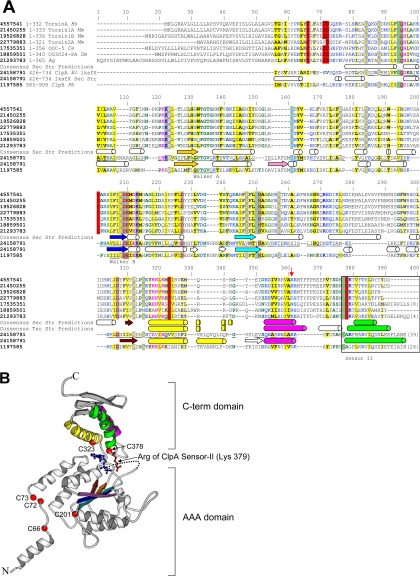
Figure 1.
General structural model of C. elegans OOC-5 and other members of the torsin family. (A) Alignment of torsin proteins with E. coli ClpA, a protein of known structure. C. elegans OOC-5, human torsinA, and five close homologues, aligned using T-COFFEE, are shown on the first seven lines. The consensus secondary structure prediction for these proteins using three methods, as described in the text, are displayed on the eighth line; predicted helices are shown as cylinders and predicted strands are shown as arrows. NCBI gi identifiers are shown in bold type, ranges of sequence numbering included in the alignment are given immediately thereafter, and species abbreviations are shown in italics. Sequences from E. coli ClpA and P. berghi ClpB, found using database searches as described in the text, are shown on lines 9 and 11, respectively. These two sequences have been aligned to human torsinA, and thus implicitly to OOC-5 and the other torsin proteins, through a shared conserved domain database (CDD) profile, as described in the text. The portions of the ClpA sequence that align to human torsinA are underlined. The experimentally determined secondary structure of ClpA (PDB 1ksfX) is shown below its corresponding sequence. Consensus tertiary structure predictions of the smaller C-terminal domain only, using ROSETTA, are displayed below the secondary structure predictions for this domain. Colors of secondary structure elements correspond to colors in B. The alignment was colored automatically using CHROMA; sites of predominately hydrophobic character are yellow, whereas sites of predominantly charged or polar character are blue. Six conserved cysteines predicted to form at least two disulfide bonds in the torsin proteins are highlighted in red. Positions 1-55 of the alignment (corresponding to position 1-34 of torsinA) are not reliably aligned. (B) Locations of six cysteine residues in the torsin family and the inferred Sensor-II motif mapped onto the E. coli ClpA structure (PDB 1ksfX). Conserved cysteines are shown as red spheres and are numbered as in A. The Arg 702 side chain of E. coli ClpA, aligned to the Lys of the C. elegans OOC-5 sequence at position 379 in Figure 1A, is explicitly shown in red. The ADP observed in the ClpA active site is shown in blue.