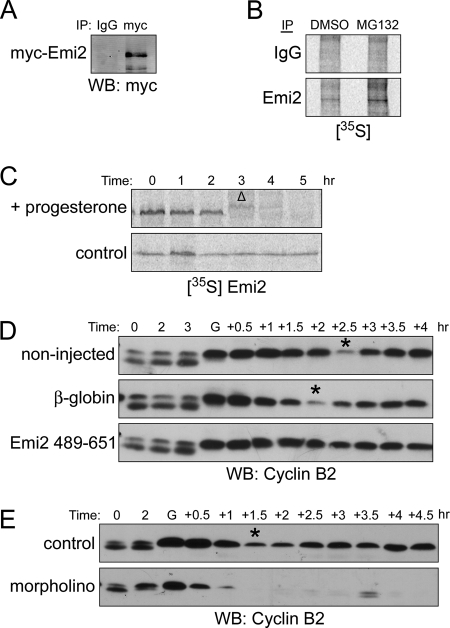
Figure 1.
Translation and degradation of Emi2 in MI. (A) Oocytes were injected with Myc6-Emi2–3′-UTR mRNA and incubated overnight (0.3 ng/oocyte). Oocytes were treated with progesterone and monitored visually for GVBD. One hour after GVBD, oocytes were lysed, and lysates were incubated with anti-Myc or IgG coupled to protein A Sepharose beads for 2 h at 4°C. The beads were retrieved, washed, and treated with lambda phosphatase before Western Blot analysis. (B) One hundred oocytes were treated with 200 μM Mg132 or DMSO in the presence of 400 μCi [35S]methionine/cysteine. One hour after GVBD, oocytes were lysed, and lysates were incubated with anti-Emi2 or IgG coupled to protein A Sepharose beads for 2 h at 4°C. The beads were retrieved, washed and treated with lambda phosphatase before analysis by autoradiography. (C) 35S-labeled Emi2 was injected into oocytes that were subsequently treated with or without progesterone. At the indicated times, lysates were made and analyzed by autoradiography after SDS-PAGE. GVBD was monitored visually. Δ, GVBD. (D) Oocytes were injected with either β-globin or Flag-Emi2 (489-651) mRNA appended with β-globin 3′-UTR (0.3 ng/oocyte). After overnight incubation, oocytes were treated with progesterone. At the indicated times, lysates were made and analyzed by Western blotting. Asterisks indicate the transition from MI to MII. GVBD was monitored visually. G, GVBD. (E) Oocytes were injected with either Emi2 morpholino (20 μM) or control morpholino (20 μM). After 1-h incubation, oocytes were treated with progesterone. At the indicated times, lysates were made and analyzed by Western blotting. Asterisks indicate the transition from MI to MII. GVBD was monitored visually. G, GVBD.