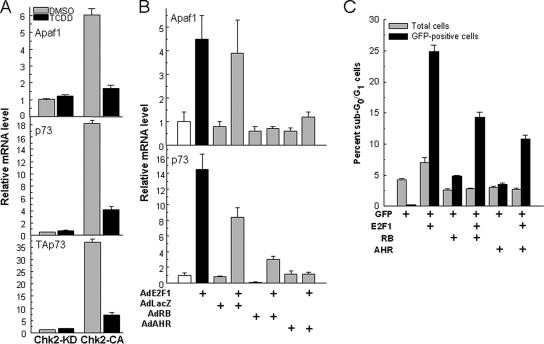
Figure 4.
AHR-E2F1 interactions repress Apaf1 and p73 expression and inhibit apoptosis. (A) Ligand activation of the AHR represses CHK2-dependent induction of Apaf1 and p73. Mouse hepatoma Hepa-1 cells were transfected with a constitutively active CHK2 expression plasmid (CHK2-CA) or its kinase-dead counterpart (CHK2-KD). After selection for 10 d in G418, cells were treated with 5 nM TCDD or with DMSO vehicle, and 12 h later they were harvested and total RNA was extracted for determination of mRNA levels of Apaf1, p73, using both primers that detect transcripts common to TAp73 and DNp73 (middle) and primers specific for TAp73 (bottom), and β-actin control by real-time RT-PCR. The values shown are the mean ± SD of three determinations relative to β-actin. (B) AHR and RB overexpression inhibit Apaf1 and p73 induction by overexpression of E2F1. Saos-2 cells were infected with 100 pfu/cell of the adenoviral expression vectors AdE2F1, AdLacZ, AdRB, and AdAHR in the combinations indicated in the figure. RNA was extracted 24 h after infection and used to determine mRNA levels of Apaf1, p73 and β-actin control by real-time RT-PCR. The values shown are the mean ± SD of three determinations relative to β-actin. As shown previously (Puga et al., 2000; Marlowe et al., 2004) no ligand is necessary to activate the AHR in these cells. (C) AHR and RB inhibit apoptosis induction by E2F1. Saos-2 cells were transfected with plasmid vectors for expression of E2F1, GFP fused to histone H2B, RB, and AHR in the combinations indicated in the figure. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry after propidium iodide staining. Total and GFP-positive sub-G0/G1 cells were scored separately to discriminate between the total and the transfected cell populations.