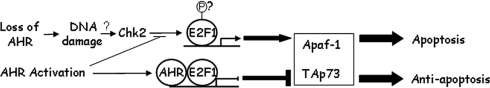
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the outcome of AHR–E2F1 interactions. DNA damage, in general, or specifically due to loss of AHR, causes induction of the E2F1 apoptotic pathway, which proceeds through CHK2 activation, E2F1 phosphorylation, induction of proapoptotic genes, and apoptosis. The question marks indicate that at present we do not know whether CHK2 activity and E2F1 phosphorylation also result from AHR loss. AHR activation causes it to complex with E2F1 and block proapoptotic gene induction by blocking CHK2 phosphorylation of E2F1, ultimately leading to an antiapoptotic endpoint.