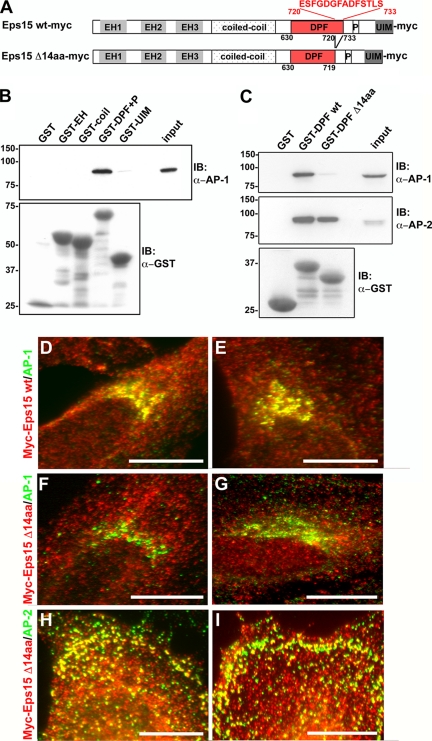
Figure 3.
The interactions between Eps15 and the clathrin adaptors AP-1 and AP-2 are mediated by distinct domains of Eps15. (A) Schematic representation of the Myc-tagged wild-type and 14-amino acid deletion mutant Eps15 proteins used in this study. The indicated Eps15 protein domains include: three Eps15 homology (EH) domains, a coiled-coil domain, a region rich in aspartate-proline-phenylalanine (DPF) repeats, a proline-rich region (P), and two ubiquitin-interacting motifs (UIM). A 14-amino acid region in the C-terminal region of the DPF repeats domain has been predicted to bind to AP-1 (Duncan and Payne, 2003) and was deleted as shown. (B and C) GST fusion proteins of the different Eps15 domains, as indicated, were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads and incubated with HeLa cell lysates. The proteins bound by the different Eps15 domains were then analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against AP-1 (B and C) and AP-2 (C). As a control, samples were also immunoblotted for GST to detect the amount of GST-tagged protein loaded (B and C). The GST fusion proteins containing the full-length DPF repeats domain of Eps15, either in combination with the proline-rich region (GST-DPF+P, B) or alone (GST-DPF wt, C), were able to pull down AP-1 and -2. In contrast, GST fusion proteins of the DPF repeats domain deletion mutant lacking the C-terminal 14 amino acids (GST-DPF Δ14aa) no longer pulled down AP-1, whereas the association with AP-2 was maintained (C). The input lanes represent 5% of the total cell lysates used for the pulldown. (D–I) The 14-amino acid motif at the C-terminus of the DPF repeats domain is necessary for the Eps15–AP-1 interaction at the trans-Golgi network within cells. HeLa cells expressing either Eps15 wt-myc (D and E) or Eps15 Δ14aa-myc (F–I) were immunostained for Myc (D–I, red) and AP-1 (D–G, green) or AP-2 (H and I, green). In agreement with the pulldown assays, significant overlap was not detected between the Eps15 deletion mutant, Eps15 Δ14aa-myc, and AP-1 at the Golgi (F and G; compare with Eps15 wt-myc and AP-1 shown in D and E), whereas the colocalization with AP-2 at the plasma membrane was maintained (H and I). Scale bars, 20 μm.