Figure 3.
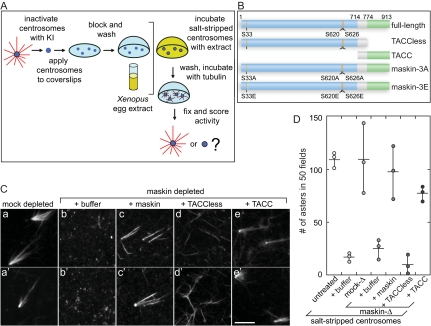
Maskin is required for centrosome function. (A) Schematic diagram of the centrosome complementation assay. Salt-stripped centrosomes are applied to a coverslip and incubated with Xenopus egg extract. The extract is washed away and the centrosomes are challenged with purified bovine tubulin. The samples are then fixed and scored for activity. (B) Schematic diagram of the maskin constructs used in this study. The conserved TACC domain (amino acids 714–931) is shown in green, the TACCless domain (amino acids 1–774) is blue. The overlap between the TACC and TACCless domains is gray. The highlighted Aurora A phosphorylation sites (S33, S620, and S626) were mutated to glutamic acids (maskin-3E) or alanines (maskin-3A). (C) Centrosome activity can be reconstituted if salt-stripped centrosomes are incubated with maskin-depleted extracts containing recombinant full-length maskin or TACC domain. Centrosomes were salt-stripped and incubated with extracts supplemented with recombinant proteins (or buffer) as indicated above the micrographs. Two representative micrographs per complemented centrosomes are shown. Bar, 10 mm. (D) Quantification of centrosome activity in the complementation assay, expressed as the number of asters found in 50 randomly selected microscope fields. The results for three independent experiments are shown (circles). The average is represented as a horizontal line. Vertical lines indicate the spread of the data. Conditions are indicated below the graph.