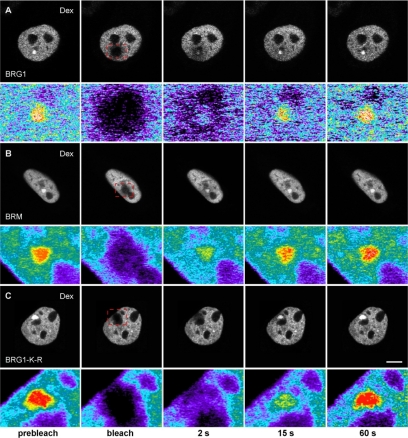
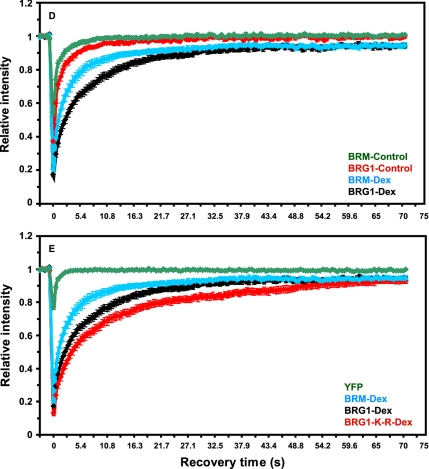
Figure 6.
Chromatin remodeling complexes have distinct kinetic properties and dynamically associate with MMTV-LTR array in a ligand and ATPase-dependent manner. (A–C) Qualitative FRAP analysis of BRG1, mutant BRG1-K-R and BRM in 1365.1 cells. 1365.1 mouse fibroblast cells were transfected with YFP-BRG1, YFP-BRG1-K-R, or GFP-BRM and treated with 100 nM dexamethasone for 30 min. BRG1 (A), BRM (B), or BRG1-K-R (C) bound to the MMTV-LTR array was imaged before and during recovery after photobleaching of the array for 120 ms. Images were acquired at the indicated times after the end of the bleach pulse. The MMTV-LTR array and the area of the bleached region is indicated by a red rectangle and shown as an enlarged pseudocolor image in the bottom panels. (D) Quantitative FRAP analysis of YFP-BRG1 or GFP-BRM in the nucleoplasm (control) or bound to the MMTV-LTR array after treatment with dexamethasone for 30 min (Dex). BRG1 and BRM bound to the MMTV-LTR array showed slower recovery kinetics after ligand treatment. (E) Quantitative FRAP analysis of YFP-BRG1, YFP-BRG1-K-R, or GFP-BRM bound to the MMTV-LTR array after treatment with dexamethasone for 30 min. The recovery kinetics of mutant BRG1-K-R bound to the MMTV array was slower than the wild-type BRG1 or wild-type BRM bound to MMTV-LTR array. All quantitative data values in the FRAP studies represent averages ± SE from at least 25 cells imaged in three independent experiments. Bar, 4 um.