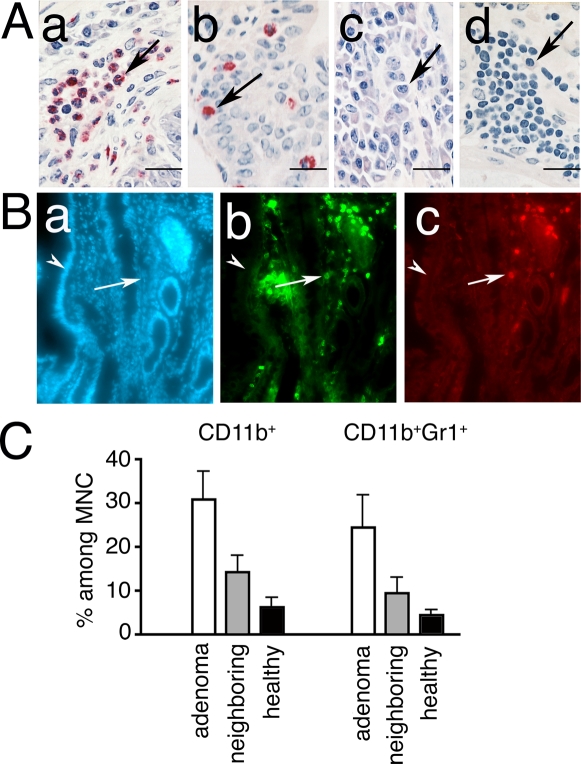
Figure 1. Infiltration of polyps by pro-inflammatory cells.
(Α) Histology of polyps from APCΔ468 mouse. (a–b) CEA stained paraffin sections counterstained with Gill's II Hematoxylin; (c&d) methylene blue staining; arrows point to (a) granulocytes, (b) mast cells, (c) plasma cells, (d) lymphocytes. (B) Immuno-fluorescence of polyps from APCΔ468 mice. Cryosections were stained with (a) DAPI, (b) CD11b-AlexaFluor 488, and (c) Gr1-AlexaFluor 594. Arrows point to polyp, and arrowheads to the adjacent healthy villus; note accumulation of CD11b+ cells and/or Gr1+ cells in the polyps. (C) FACS analysis of leukocytes prepared from micro-dissected polyps, and from adjacent tissue (n = 4), and of intestinal tissue from age-matched healthy control mice (n = 3). Mean values and SEM are shown for frequencies of CD11b+ and of CD11b+Gr1+ cells in 6 month-old mice.