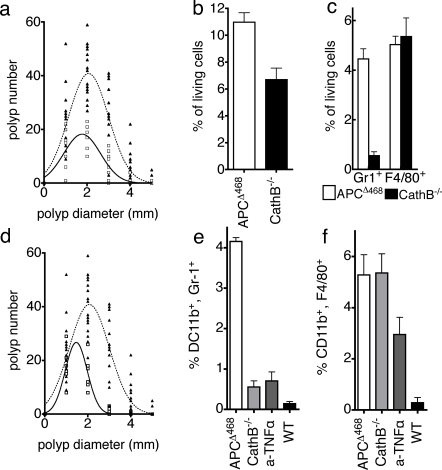
Figure 6. Cathepsin B deficiency or anti-TNFα treatment attenuate polyposis.
(a) Non-linear regression analysis of polyp number and diameter, assuming Gaussian distribution; APCΔ468 Ctsb−/− (continued line, open squares), and APCΔ468 (dotted line, closed triangles). Note that Cathepsin B−/− mice had fewer and smaller polyps. (b) Frequencies of ProSense-680 active leukocytes amongst total MNCs prepared from the intestine of APCΔ468 (open bar, 6.7%±086%) or APCΔ468Ctsb−/− (filled bar, 11%±0.69%, P = 0.0037; unpaired t test with Welsh correction). (c) Frequencies of ProSense-680 active CD11b+Gr1+ (mean 0.56%) or CD11b+F4/80+ (mean 4.46%) cells, from the intestines of APCΔ468 (open bar) and APCΔ468Ctsb−/− mice (filled bars); P<0.001, n = 6, 2way ANOVA. Note that Cathepsin B deficiency predominantly impacted the abundance of CD11b+Gr1+ cells. (d) Attenuation of polyposis in anti-TNFα treated mice (solid line, open squares, n = 6), as compared to the APCΔ468 (dotted line & closed triangles). (e) Frequencies of CD11b+Gr1+ amongst total intestine live MNCs; APCΔ468Ctsb−/− intestine (light gray bar, 0.56±0.15%, P<0.001), anti-TNFα treated (dark gray bar, 0.71±0.22%, P<0.001), untreated APCΔ468 (open bar, 4.2±0.093%), wt control intestine (black bar, 0.15±0.051%). (f) Frequencies of CD11b+F4/80+ in the APCΔ468 (5.03±0.78%), APCΔ468Ctsb−/− intestine (5.36±0.92%), and anti-TNFα treated intestine (dark gray bar, 3.0±0.67%).