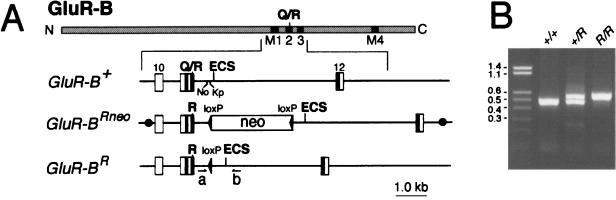
Figure 1.
GluR-B alleles having an exonic arginine codon for the inner pore segment of AMPAR channels. (A) Schematic representation of the GluR-B subunit and of GluR-B gene segments corresponding to different alleles: GluR-B+ (wild-type allele), GluR-BRneo (targeted allele), and GluR-BR (targeted allele after Cre-mediated removal of the floxed neo cassette). In the GluR-B protein (hatched), the N and C termini and the Q/R site are indicated; black boxes mark membrane insertion domains M1–M4. The GluR-B gene segments show numbered exons (boxes), the exon-complementary, cis-acting ECS element in intron 11, the position of the Q/R site, the location of the exonic arginine (R) codon for the Q/R site, as well as the locations of primers MH53 (a) and RSP36 (b) used for genotyping. The loxP sites are shown as filled arrowheads. The floxed PGK-neo marker in the GluR-BRneo allele was inserted between intronic NcoI (No) and KpnI (Kp) sites. • in the GluR-BRneo allele border the targeting vector (BsrGI-SalI fragment). (B) Genotyping by PCR. The expected sizes of amplicons for wild-type and GluR-BR alleles are 494 and 599 bp, respectively. Genotypes are indicated on top of gel, size markers are given in kbp on left of gel.