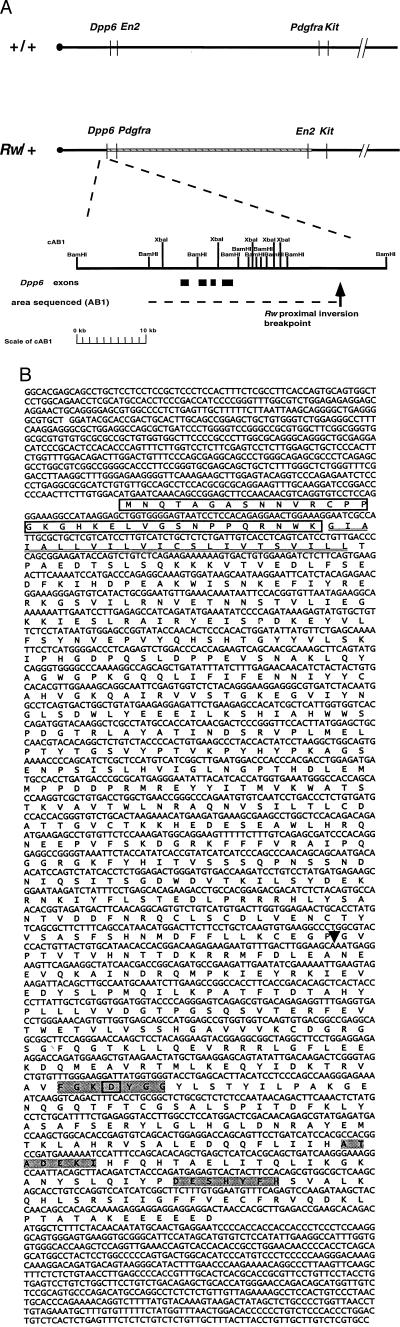
Figure 3.
Genomic structure of the proximal Rw inversion breakpoints. (A) Wild-type and Rw chromosomal maps give the approximate map positions of genes based on previous studies (14, 22, 31). The Rw inversion is represented by a cross-hatched box. Cosmid cAB1 was isolated by screening a genomic library of Rw/+ DNA with a unique probe from cRBH5 (D5Buc4) as described in the text. Chromosomal distances are not represented on scale. The restriction map of cAB1 is shown. Dashed lines indicate the sequenced region. Solid lines below cAB1 give the approximate positions of Dpp6 exons found by sequencing and grail2 analysis. Arrow shows the positions of the inversion breakpoint. (B) Sequence analysis of the embryonic Dpp6 cDNA (GenBank accession no. AF092507). Shown are the cDNA sequence and the deduced amino acid sequence. The putative intracellular domain is boxed and the transmembrane domain double underlined. The first 20 amino acids are unique in the embryonic DPP6 isoform. The conserved residues, which form the putative catalytic site in nonclassical serine peptidases, are gray shaded, and the aspartic residue, which is replaced by a serine residue shown to be essential for peptidase activity in DPP4, is boxed (32). The location of the proximal Rw inversion breakpoint, which eliminates the C-terminal portion of DPP6, is indicated by an arrowhead.