Figure 1.
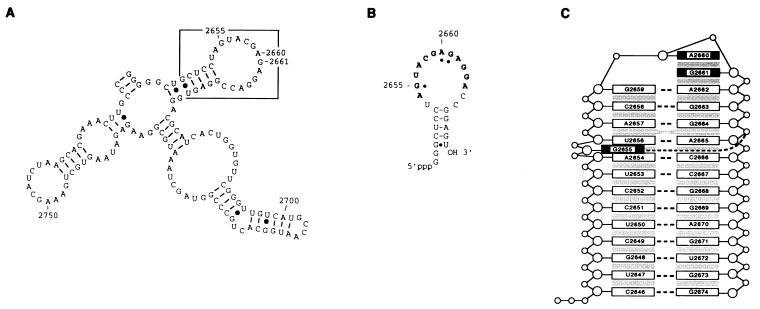
The S/R domain of 23S rRNA. (A) A portion of E. coli 23S rRNA with the S/R domain boxed. (B) An S/R oligoribonucleotide (a 27-mer) that mimics the sequence of the domain (nucleotides 2648–2672) and has in addition two 5′ guanosine residues that derive from the T7 promoter used to transcribe the RNA. The universal sequence is in boldface letters and the nucleotides protected from chemical modification by EF-G are designated by dots. (C) Representation of the three-dimensional conformation of an E. coli S/R domain oligoribonucleotide determined by NMR spectroscopy (K. Seggerson and P. Moore, personal communication) and based on the NMR determined structure of the closely related eukaryotic S/R domain RNA (14, 15). The numbering is the positions of nucleotides in E. coli 23S rRNA.