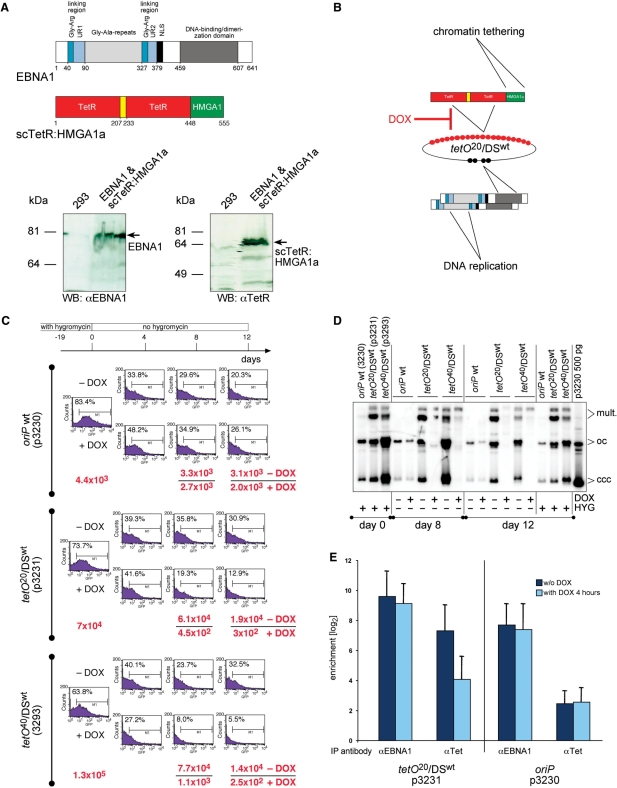
Figure 2.
scTetR:HMGA1a confers conditional plasmid maintenance. (A) The trans-acting factor scTetR:HMGA1a consists of a single-chain (sc) dimer of two tetR genes joined via an artificial linking domain (yellow) which was fused to the HMGA1a coding sequence. Western blot analysis of the parental HEK293 cells and its derivative expressing EBNA1 + scTetR:HMGA1a with TetR- and EBNA1-specific antibodies. (B) scTetR:HMGA1a and EBNA1 mediate chromatin tethering and DNA replication, respectively. (C) DOX downregulates vector-encoded GFP expression and causes induced loss of plasmid DNA. The oriP wt (p3230) plasmid and two hybrid replicon plasmids tetO20/DSwt (p3231) and tetO40/DSwt (p3293) were transfected into EBNA1 and scTetR:HMGA1a expressing HEK293 cells, which were then selected with hygromycin for 19 days. At that time point (day 0) selection was removed and the cells were further cultivated with or without DOX (2.5 g/ml) for 12 days. On days 0, 4, 8 and 12, cells were analyzed by FACS for the expression of plasmid-encoded GFP. Plasmid rescue experiments were performed on days 0, 8, and 12. Low-molecular weight DNAs were prepared and cleaved with DpnI and 600 ng of each DNA sample was electroporated into E. coli DH10B. The absolute numbers of ampicillin-resistant colonies were calculated and shown in red as indicated (−/+DOX). (D) Hybrid replicon plasmids are maintained as plasmids in the absence but precipitously lost in the presence of DOX. As in C, p3230 (oriP wt) and two plasmids p3231 (tetO20/DSwt) and p3293 (tetO40/DSwt) were transfected and selected. Low-molecular weight DNA was prepared on days 0, 8, and 12. DNA was also prepared from the same cells, which had been kept under continuous hygromycin selection (HYG). The DNAs were digested with DpnI to multiply cleave unreplicated DNAs and PmlI to cut cellular DNA, only. Southern blot hybridization were performed as in Figure 1C. The rightmost lane indicates the migration pattern of 500 pg E. coli-derived p3230 plasmid DNA indicating monomeric supercoiled, covalently closed and circular (ccc), monomeric open circles (oc) and multimeric (mult.) forms of plasmid DNA. The ccc and oc form DNAs indicate the presence of extrachromosomal plasmids for a period of 31 days throughout the entire experiment. Upon addition of DOX, the hybrid replicon plasmids were precipitously lost. In the absence of DOX, they were maintained at higher copy numbers than wild-type oriP. (E) ChIP experiments indicate DOX-induced loss of DNA binding of scTetR:HMGA1a but not EBNA1. From formaldehyde crosslinked chromatin of stably transfected cells as in C, EBNA1 and scTetR:HMGA1a were immunoprecipitated and the precipitates were analyzed for coprecipitated plasmid DNA molecules by quantitative real-time PCR. The histogram shows the results for p3231 (tetO20/DSwt) and p3230 (oriP wt) without or with DOX for 4 h. The columns indicate the difference between PCR data (mean values and standard deviations of three experiments) obtained with specific antibodies versus isotype control and preimmune serum on a logarithmic y-axis.