Figure 1.
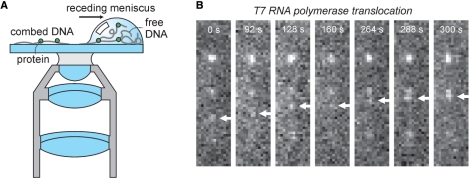
Immobilizing DNA on a surface by combing. (A) Cartoon of the combing procedure. DNA can be stretched and immobilized using hydrophobic silanized glass surfaces and a receding air–water interface. After rehydration of the sample the DNA stays firmly attached to the glass slide. Combing can also be achieved using fluid flow which results in lower stretching forces. (B) Kim and Larson visualized in real time the motion of T7 RNAP along combed DNA strands (9). The directional movement of the T7 RNAP elongation complex along a DNA molecule is observed using the incorporation of fluorescent UTP into RNA strand. Adapted by permission of Oxford University Press from Ref. (9).