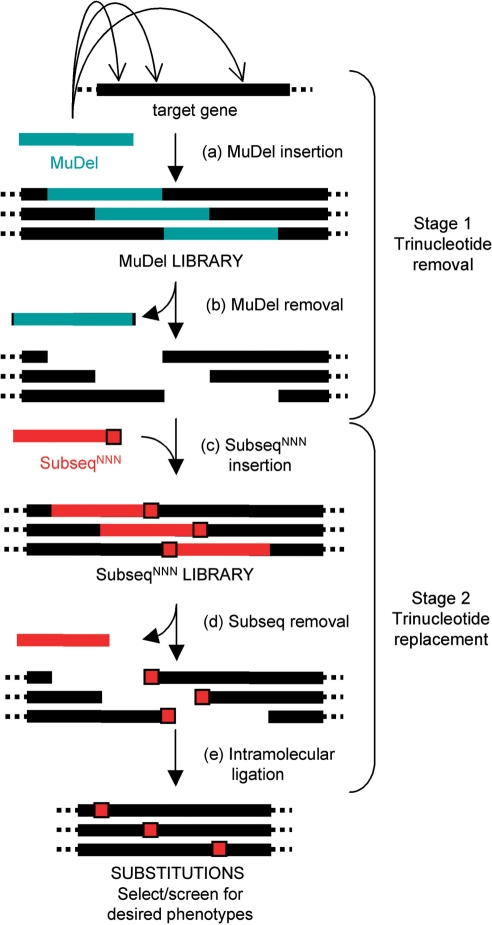
Figure 1.
Schematic outline of the TriNEx procedure. Stage 1. Trinucleotide deletion. The MuDel library is generated by in vitro transposition of the engineered transposon MuDel (teal) into the target DNA. Restriction endonuclease digestion removes MuDel from this library together with 3 bp of the original target DNA to generate a single break per molecule. Stage 2. Trinucleotide replacement. The DNA cassette termed SubSeqNNN (red) is then inserted between the break in the target DNA to generate the SubSeqNNN library. The last three nucleotides at one end of SubSeqNNN (red square) are randomized (NNN). Restriction endonuclease digestion removes all SubSeq, except for the NNN sequence that is now incorporated into the target DNA, which replaces the 3 bp deleted in stage 1. Intramolecular ligation regenerates the complete gene containing new and randomly placed trinucleotide segments. This is followed by selection and/or screening to identify new variants with desired properties.