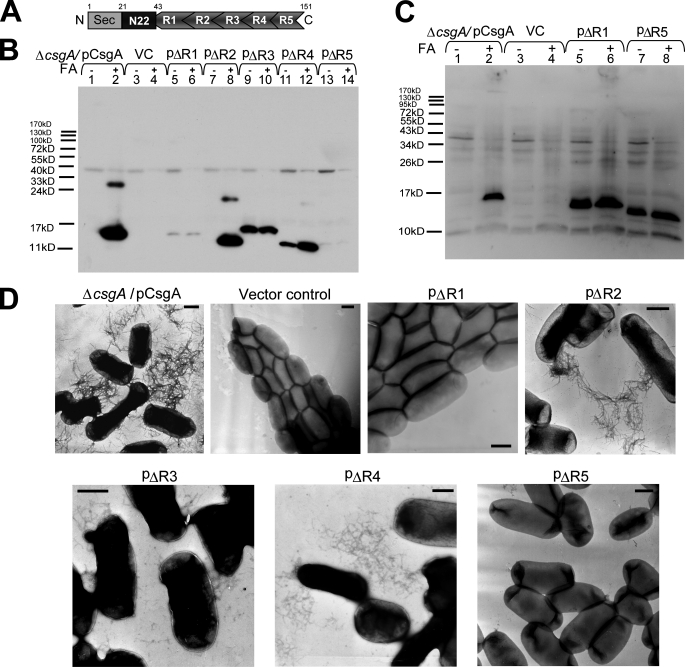
FIGURE 1.
R1 and R5 are critical for CsgA in vivo polymerization into an amyloid fiber. A, schematic of CsgA including an N-terminal Sec signal peptide and the N-terminal 22 residues that precede the five repeating units. N, N terminus; C, C terminus. B, whole-cell Western blots of csgA mutant strains harboring the following plasmids: pCsgA (lanes 1 and 2), vector control (VC) (lanes 3 and 4), pΔR1 (lanes 5 and 6), pΔR2 (lanes 7 and 8), pΔR3 (lanes 9 and 10), pΔR4 (lanes 11 and 12), and pΔR5 (lanes 13 and 14). Samples were treated with (+) or without (-) FA. The blot was probed with anti-CsgA antibody. C, Western blot of whole cells and underlying agar (agar plugs) from csgA strains containing constructs pCsgA (lanes 1 and 2), vector control (lanes 3 and 4), pΔR1 (lanes 5 and 6), and pΔR5 (lanes 7 and 8) grown 48 h at 26 °C on YESCA plates. Samples were treated with (+) or without (-) FA. The blots were probed with anti-CsgA antibody. D, negative-stain EM micrographs of csgA mutant cells containing the indicated plasmids. Cells were grown on YESCA plates for 48 h at 26 °C prior to staining with uranyl acetate. Scale bars are equal to 500 nm.