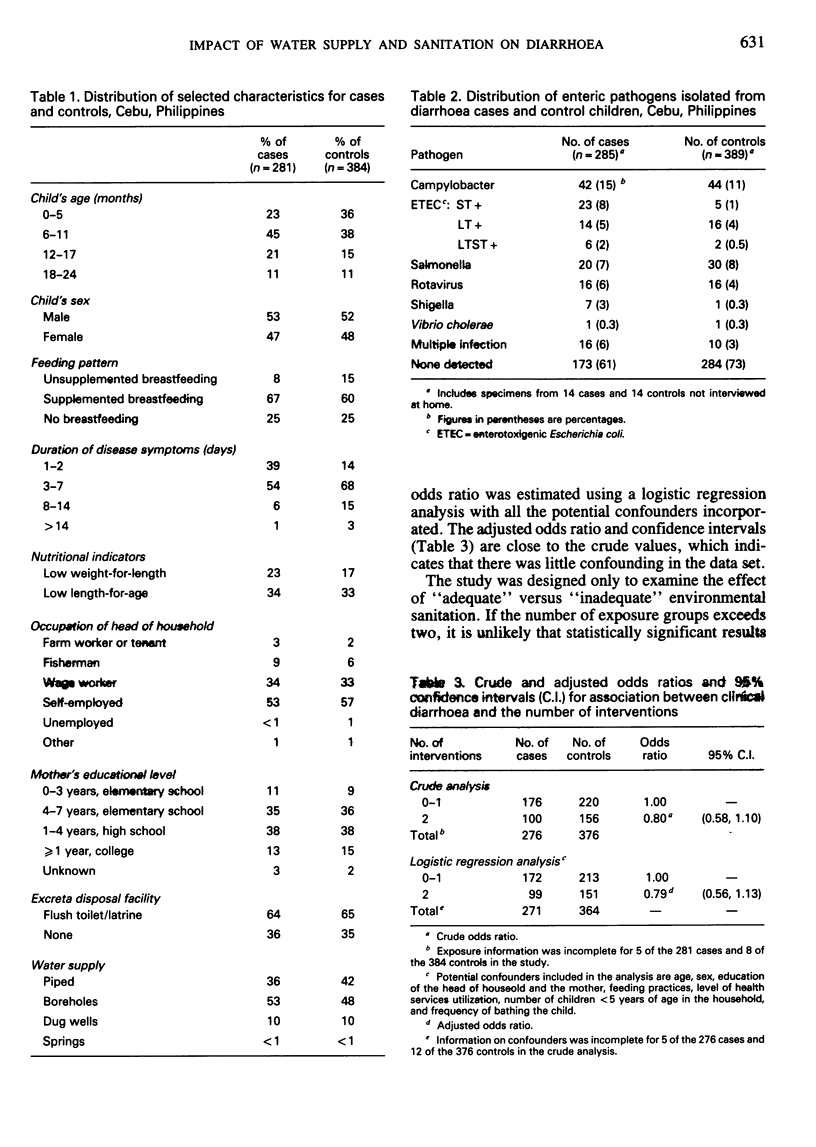
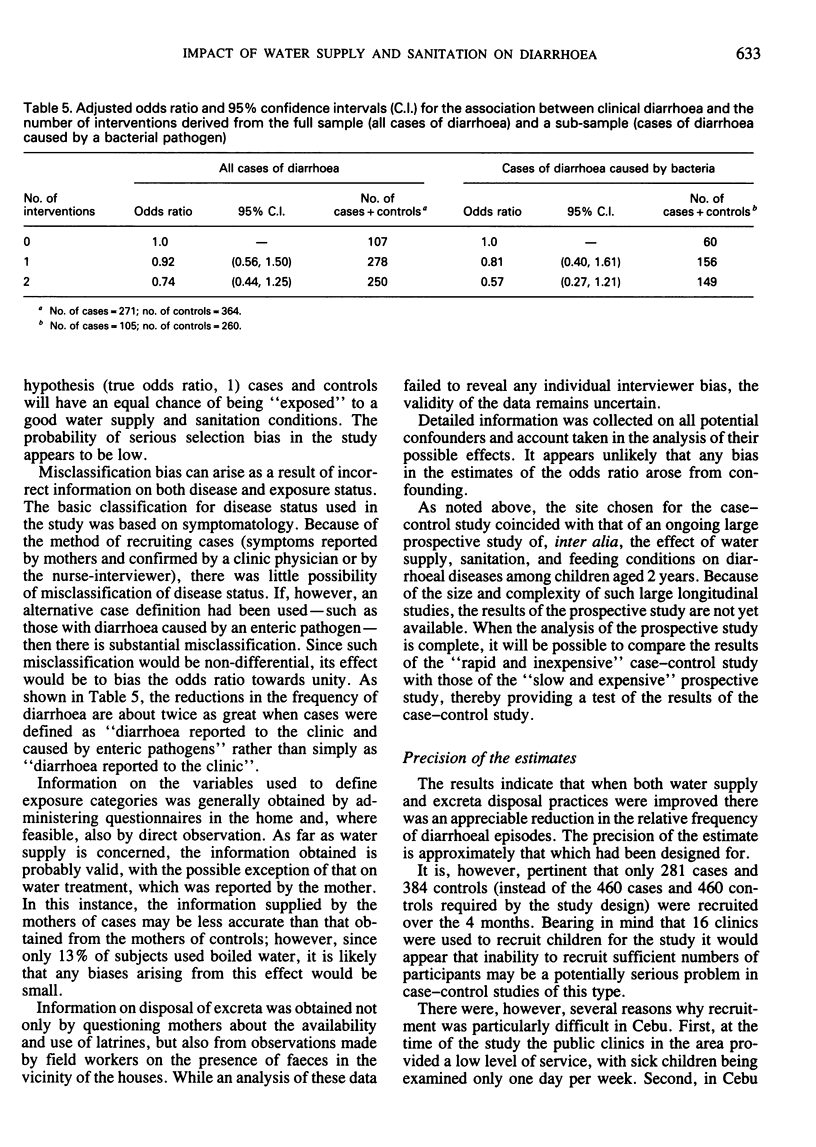
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blum D., Feachem R. G. Measuring the impact of water supply and sanitation investments on diarrhoeal diseases: problems of methodology. Int J Epidemiol. 1983 Sep;12(3):357–365. doi: 10.1093/ije/12.3.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briscoe J. Intervention studies and the definition of dominant transmission routes. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 Sep;120(3):449–455. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butz W. P., Habicht J. P., DaVanzo J. Environmental factors in the relationship between breastfeeding and infant mortality: the role of sanitation and water in Malaysia. Am J Epidemiol. 1984 Apr;119(4):516–525. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleiss J. L. Significance tests have a role in epidemiologic research: reactions to A. M. Walker. Am J Public Health. 1986 May;76(5):559–560. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.5.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuval H. I., Tilden R. L., Perry B. H., Grosse R. N. Effect of investments in water supply and sanitation on health status: a threshold-saturation theory. Bull World Health Organ. 1981;59(2):243–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker A. M. Reporting the results of epidemiologic studies. Am J Public Health. 1986 May;76(5):556–558. doi: 10.2105/ajph.76.5.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterlow J. C., Buzina R., Keller W., Lane J. M., Nichaman M. Z., Tanner J. M. The presentation and use of height and weight data for comparing the nutritional status of groups of children under the age of 10 years. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(4):489–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young B., Briscoe J. A case-control study of the effect of environmental sanitation on diarrhoea morbidity in Malawi. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1988 Mar;42(1):83–88. doi: 10.1136/jech.42.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Zoysa I., Feachem R. G. Interventions for the control of diarrhoeal diseases among young children: rotavirus and cholera immunization. Bull World Health Organ. 1985;63(3):569–583. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


