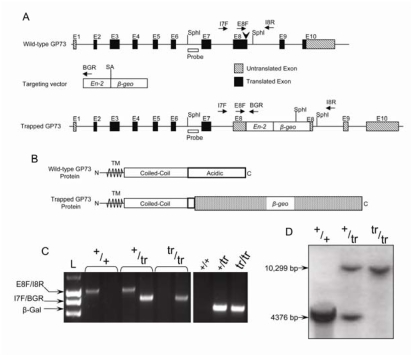
Figure 1.
Generation of mice with a truncated GP73 gene. A. Top: Map of the wild-type mouse GP73 gene. SphI cleavage sites, vector insertion site (arrowhead), Southern probe, and genotyping primers (arrows) are indicated. Middle: The gene-trap targeting vector is depicted with the splice acceptor (SA) of the mouse En-2 gene and the β-geo reporter sequences. SphI cleavage site and the reverse genotyping primer are indicated. Bottom: The mutant GP73 allele following insertion of the gene trap vector. B. Top: Predicted wild-type GP73 protein with the transmembrane domain (TM), and C-terminal coiled-coil and acidic domains shown. Bottom: Predicted GP73/β-Geo fusion protein with C-terminal truncation of GP73. C. Left: PCR genotyping of GP73+/+ GP73+/tr, and GP73tr/tr mice. Primer pairs used to generate each PCR product are indicated. Right: PCR-amplification of β-gal sequence from GP73+/+, GP73+/tr, and GP73tr/tr mice. D. Southern blot of GP73+/+, GP73+/tr, and GP73tr/tr mice. The 4376 bp fragment generated from the GP73+/+ allele, and 10,299 bp fragment generated from the GP73tr/tr allele are indicated.