Figure 1.
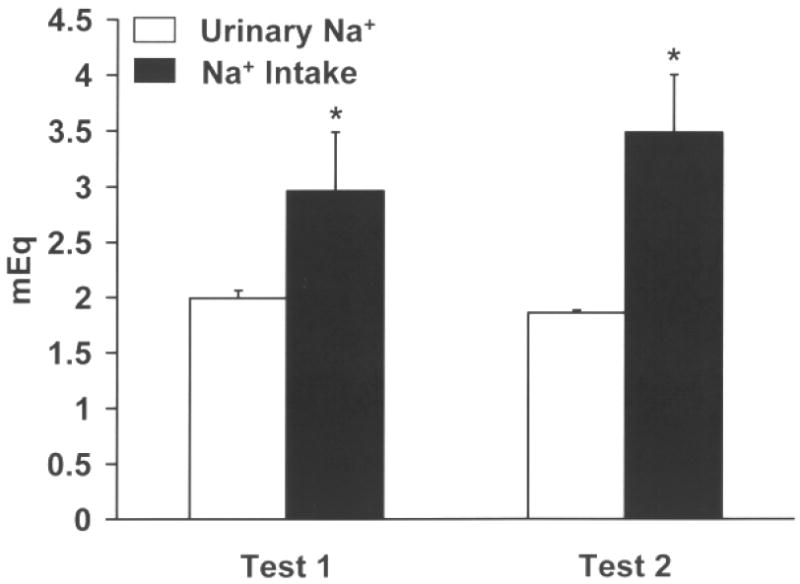
Mean (+) SEM urine (Na+) output (white bars) and saline (Na+) intake (black bars) values expressed as mEq of sodium after two acute furosemide depletions. Rats were sodium depleted two times, each depletion spaced one week apart. Twenty four hour urine samples were collected beginning immediately following the diuretic/natriuretic treatment. Rats with water available continuously were given access to 0.3 M saline for 2 h the next day and intake was recorded. Intakes of saline were compared against urine output. During tests 1 and 2, rats consumed more than Na+ was necessary to restore the sodium deficit caused by furosemide treatment. * p<0.05
