Figure 3.
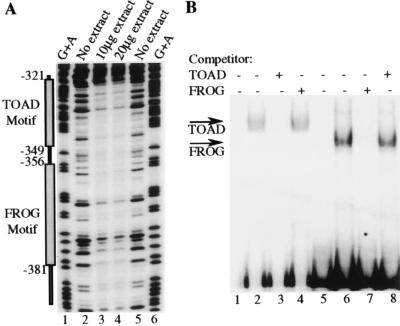
B29 5′ silencer elements interact with DNA binding proteins. (A) The endpoint of the DNase I footprints are identified by nucleotide numbers with respect to the start site of transcription (+1). Lanes containing reactions incubated with either 10 μg or 20 μg M12 B cell crude nuclear extract are indicated (lanes 3 and 4). Lanes containing reactions incubated without extract are indicated (lanes 2 and 5). Reactions were electrophoresed alongside a G+A ladder of the probe (lanes 1 and 6). (B) Double-stranded oligonucleotides corresponding to the sequence from positions −349 to −321 (TOAD motif, lanes 1–4) and −381 to −356 (FROG motif, lanes 5–8) were end-labeled. Lanes 1 and 5 contain TOAD and FROG motif probes alone, respectively. The TOAD motif probe was incubated with 5 μg of M12 B cell nuclear extract (lanes 2–4) and the FROG motif probe was incubated with 5 μg of M12 B cell nuclear extract (lanes 6–8). Probes were incubated in the presence of a 1,000-fold excess of unlabeled TOAD motif competitor (lanes 3 and 8) or were incubated in the presence of a 1,000-fold excess of unlabeled FROG motif competitor (lanes 4 and 7). The specifically formed TOAD and FROG complexes are indicated as such with arrows.