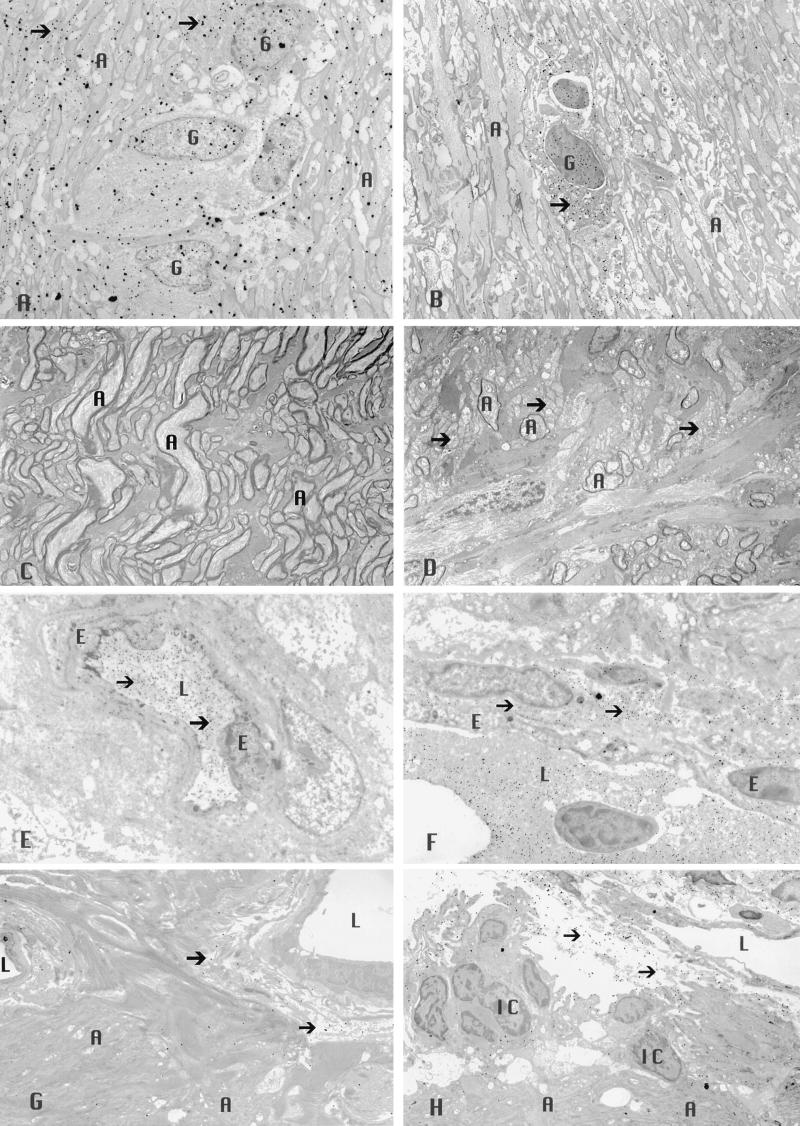
Figure 3.
Transmission electron micrographs of the optic nerve showing increased levels of catalase immunogold (arrows) are evident within the cytoplasm and nuclei of glial cells and within axons after rAAV-Cat inoculation (×2,500) (A), relative to that seen with rAAV-gfp inoculation (×2,500) (B). Less demyelinated axons were evident with rAAV-Cat inoculation (×2,500) (C), whereas naked axons (arrows) and those with thin sheaths of myelin were prominent in the control nerves that received rAAV-gfp (×2,500) (D). The rAAV-Cat inoculation reduced extravasation of immunogold-labeled serum albumin (arrows) that was predominantly confined to the intravascular compartment (×3,500) (E). Comparison with control nerves (inoculated with rAAV-gfp) showing marked extravasation of immunogold-labeled serum albumin (arrows) into the perivascular space (×4,000) (F). AAV catalase gene inoculation reduced in vivo levels of H2O2 (arrows) (×2,500) (G), whereas more H2O2 reaction product particles (arrows) were evident in the control nerves (×2,500) (H). A, axon; E, endothelial cell; G, glial cell; L, lumen; IC, inflammatory cell.