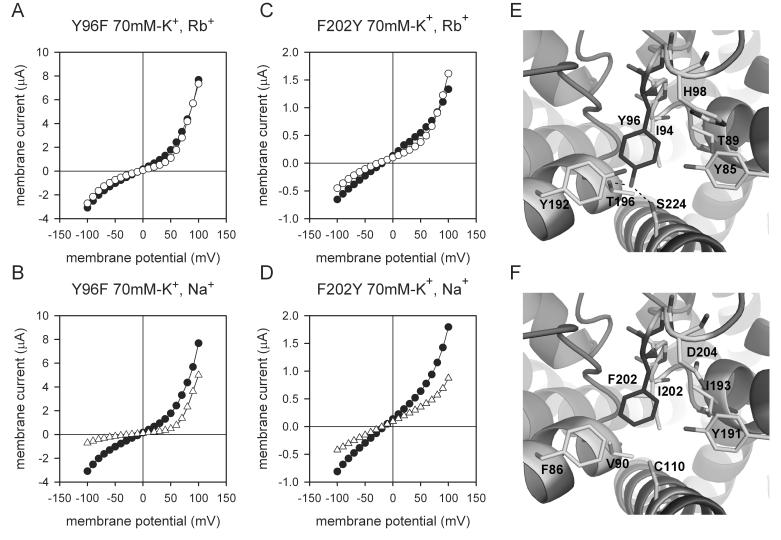
Figure 4.
Mutation Y96 and F202 of the GY(F)G triplet and ionic selectivity.
Typical current voltage relations from individual oocytes expressing the TASK-1 mutants: A, Y96F in 70mM [K+]o (●) and in 70mM [Rb+]o (○); B, Y96F in 70mM [K+]o (●) and in 70mM [Na+]o (△);C, F202Y in 70mM [K+]o (●) and in 70mM [Rb+]o (○); D, F202Y in 70mM [K+]o (●) and in 70mM [Na+]o (△); E and F. Potential interactions behind the selectivity filter suggested by our modelling studies (E) Y96 (P1) may form hydrogen bonds with T196 and S224 (depicted by dashed lines). (F) F202 (P2) is in a more hydrophobic environment than the equivalent residue in P1 (Y96), consistent with the loss of the hydroxyl. F86, V90, C110, Y191, I195, I200 and D204 surround F202.