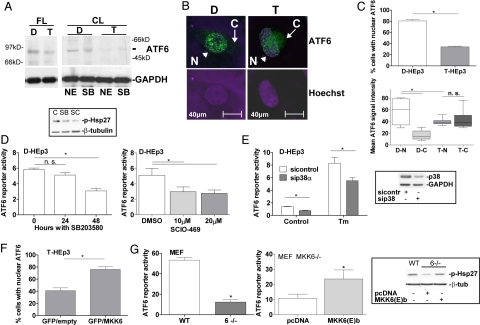
Fig. 2.
ATF6α localization in HEp3 is partly MKK6-p38-dependent. (A) Detection of full-length (FL) ATF6α by Western blot in D-HEp3 (D) and T-HEp3 (T) cell RIPA lysates (Left). Cleaved (CL) ATF6α in extracts enriched in nuclear components (commercial kit) (NE) or Laemmli buffer (SB) (Right). (B) IF for ATF6α and nuclear detection with Hoechst-33342 in D- vs. T-HEp3 [N (nuclear), arrowhead; C (cytoplasmic), arrow]. (C) Percentage of nuclear ATF6α-staining. A total of ≈300 cells in three independent experiments was scored. *, P = 0.0015 (Upper). Nuclear (N) vs. cytoplasmic (C) densitometric fluorescence quantification of ATF6α signal for D-HEp3 (D) and T-HEp3 (T) by using ImageJ. *, P < 0.05 (Lower). (D) Basal ATF6 reporter activity in D-HEp3 treated with 10 μM SB203580 (SB) for 24/48 h (Left) and 10–20 μM SCIO-469 (SC) for 48 h (Right). *, P < 0.05. The Inset shows decreased p-Hsp27 with both drugs by Western blot. (E) Basal and Tm-induced ATF6 reporter activity in D-HEp3 with and without siRNAs to p38α. *, P < 0.05. The Inset shows the level of p38 knockdown by Western blot. (F) Percentage of T-HEp3 cells with nuclear ATF6α after cotransfection of GFP with constitutively active MKK6(E)b. A total of ≈300 GFP-positive cells were scored in three experiments. *, P < 0.001. (G) Basal ATF6 reporter activity in WT or MKK6−/− MEFs (Left). *, P < 0.001. ATF6 reporter activity in MKK6−/− MEFs transfected with pcDNA3.1 or constitutively active MKK6(E)b (Right). *, P < 0.05. The Inset shows a Western blot for p-Hsp27 in these cells.