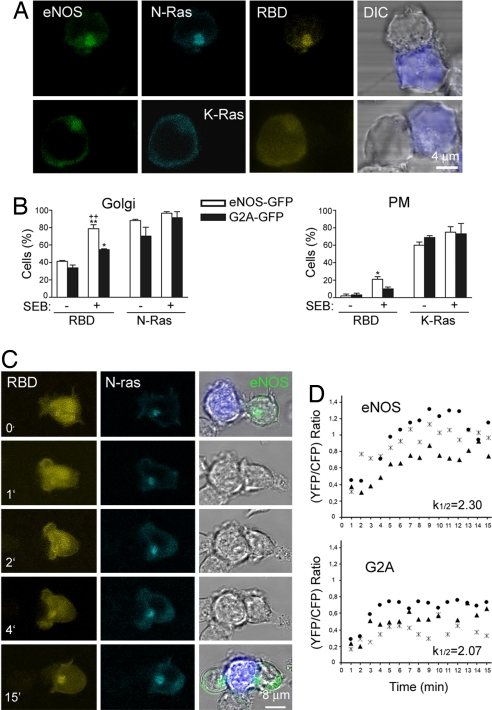
Fig. 4.
eNOS activates N-Ras on the Golgi complex of APC-conjugated T cells. (A) SEB-pulsed Raji APC were mixed with eNOS-GFP cells cotransfected with YFP-RBD-Raf-1 (RBD) and CFP-N-Ras (Upper) or -K-Ras (Lower). The subcellular localizations of eNOS (green), Ras (cyan), and RBD-Raf-1 (yellow) are shown. Raji APC (blue) was superposed on DIC images. (B) Quantitative analysis of the cellular localization of YFP-RBD-Raf-1 (RBD) in T cell–APC conjugates between naive (−) or SEB-pulsed (+) Raji APC and eNOS- or G2A-GFP cells expressing YFP-RBD-RAF-1 and CFP-N-Ras (Left) or -K-Ras (Right). Histograms show the percentages of T cells showing accumulation of YFP-RBD-Raf-1 and CFP-N-Ras on the Golgi (Left) or CFP-K-Ras at the plasma membrane (PM) (Right). More than 100 cells were scored for each condition. Data are the means ± SEM of three independent experiments. **, P ≤ 0.001; *, P ≤ 0.05 compared with nonstimulated cells; ++, P ≤ 0.001 compared with SEB-stimulated G2A-GFP cells. (C) eNOS-GFP cells transiently cotransfected with YFP-RBD-Raf-1 (yellow) and CFP-N-Ras (cyan) were mixed with SEB-pulsed Raji APC, and images were recorded by real-time confocal fluorescence microscopy at the times indicated. The fluorescence signals of eNOS (green at 0 and 15 min) and Raji APC (blue) were superposed on DIC images. (D) T cells cotransfected with CFP-N-Ras and YFP-RBD-Raf-1 were activated as in C, and the redistribution of RBD-Raf-1 toward CFP-N-Ras on the Golgi was monitored from the time of initial intercellular contacts. Three representative traces and the mean kinetic constants of YFP-RBD-Raf-1 redistribution are presented for each condition.