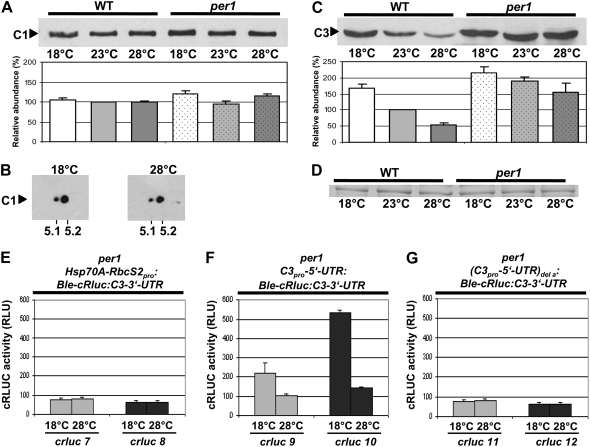
Figure 8.
In the per1 mutant, the phosphorylation degree of C1 is relatively low at both different temperatures, and the expression level of C3 is increased in comparison with that in the wild type depending on the E-box and/or the DREB1A-boxes. A, Immunodetection of C1 in per1. Cells of the per1 mutant were grown at 18°C, 23°C, and 28°C and harvested during early day (LD2). Crude extracts were prepared, and proteins (50 μg per lane) were separated by 9% SDS-PAGE along with a molecular mass standard and immunoblotted with anti-C1 antibodies (see “Materials and Methods”). Densitometry quantifications were done with three independent experiments (see “Materials and Methods”). Therefore, the amount of C1 detected in wild-type cells grown at 23°C was set to 100%. B, Immunodetection of C1 from proteins separated by 2-DE. Cells of the per1 mutant were grown at either 18°C or 28°C and harvested as described for A. Crude extracts were prepared, and proteins (300 μg per assay) were separated by standardized 2-DE (see “Materials and Methods”). For the first dimension, an IPG strip of pH 3 to 10 was taken, and in the second dimension, 10% SDS-PAGE was used along with a molecular mass standard. The proteins were then immunoblotted with anti-C1 antibodies. The positions of pH 5.1 and 5.2 that are close to the theoretical pI of C1 (5.17) are indicated. C, Immunodetection of C3 in per1. The same procedure described for A was carried out, but immunoblotting was done with anti-C3 antibodies (see “Materials and Methods”). D, A random nonspecific Coomassie blue-stained band from a duplicate gel shows that similar amounts of proteins were loaded. E to G, Measurements of cRLUC activities in different transgenic per1 cells. Lines were grown at either 18°C or 28°C and used at LD2 to measure cRLUC activities (n = 3) according to Kiaulehn et al. (2007). In the first case (E), the chimeric construct Hsp70A-RbcS2pro:Ble-cRluc:C3-3′-UTR, which is under the control of the strong Hsp70A-RbcS2 promoter and bears the c3 3′-UTR, was used for transformation of the per1 mutant, resulting in transgenic lines crluc7 and crluc8. In the second case (F), the chimeric construct C3pro-5′-UTR:Ble-cRluc:C3-3′-UTR, which is under the control of the c3 promoter region, was used for transformation of the per1 mutant, resulting in transgenic lines crluc9 and crluc10. In the third case (G), the chimeric construct (C3pro-5′-UTR)del a:Ble-cRluc:C3-3′-UTR, in which the E-box and two DREB1A-boxes had been deleted from the c3 promoter region, was transformed into the per1 mutant, resulting in transgenic lines crluc11 and crluc12.