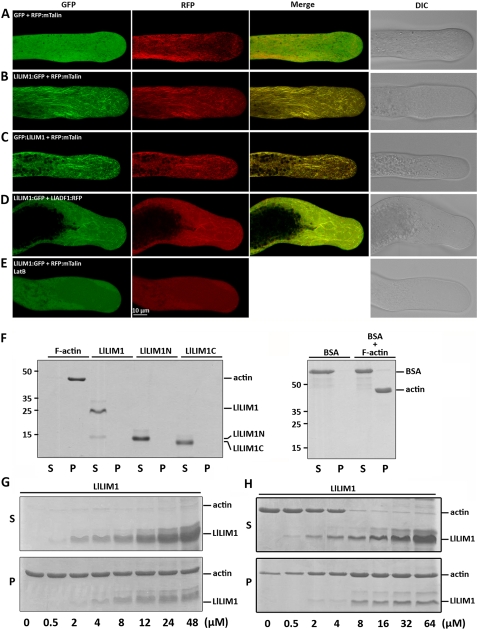
Figure 2.
LlLIM1 functions as an ABP in elongating lily pollen tubes and promote F-actin bundling, as revealed by cosedimentation assays. Confocal images show lily pollen tubes coexpressed with GFP and RFP:mTalin fusion genes (A), LlLIM1:GFP and RFP:mTalin fusion genes (B), and GFP:LlLIM1 and RFP:mTalin fusion genes (C). The images in D were from the lily pollen tube shown in C, except that the transformed pollen tubes were treated with 200 nm LatB for 1 h before recording the images. In all cases, hydrated pollen grains were cobombarded with 2.5 μg of each indicated plasmid, followed by germination in culture medium for 6 h before images were taken by fluorescent laser scanning confocal microscopy. Different fluorescent channels of images are indicated at the top of the panels. Medial sections through pollen tubes lying flat on the cover-slide surface are shown and represent at least 15 similar images collected from at least three independent experiments. DIC, Differential interference contrast. High- and low-speed cosedimentation assays were used to examine the capability for binding (G) and bundle assembly (H), respectively, of LlLIM1 recombinant proteins to F-actin. In F, 1 mg mL−1 commercial F-actin, bovine serum albumin (BSA), and the recombinant proteins indicated were added to the binding solution and centrifuged at 100,000g for 45 min. Subsequently, equal amounts of pellets (P) and supernatants (S) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie Blue staining. Only F-actin, not the remaining soluble proteins, was precipitated after high-speed centrifugation. Various amounts (0–48 μm) of LlLIM1 (G and H) and 48 μm BSA (F) were incubated with 4 μm F-actin for 1 h, then centrifuged at 100,000g (G) or 12,500g (H) for 45 min and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Equal amounts of pellets (P) and supernatants (S) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie Blue staining.