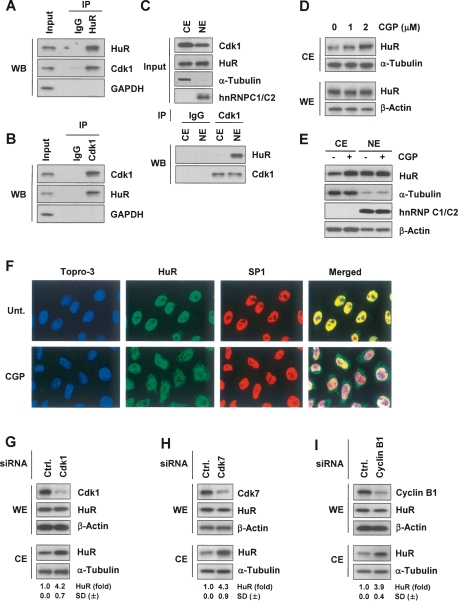
Figure 1.
Inhibition or silencing of Cdk1, an HuR-interacting protein, elevates cytoplasmic HuR levels. (A) HeLa whole-cell lysates were used in immunoprecipitation (IP) assays with either control mouse IgG or anti-HuR antibodies, followed by Western blot (WB) detection of Cdk1, HuR, and the negative control GAPDH. (B) Assays were performed as in A except that control rabbit IgG or anti-Cdk1 antibodies were used for IP. (C) Cytosolic extracts (CE) and nuclear extracts (NE) were immunoprecipitated with either control rabbit IgG or anti-Cdk1 antibodies, followed by Western blot detection of HuR and Cdk1. The levels of Cdk1, HuR, α-Tubulin (cytosolic marker), and hnRNP C1/C2 (nuclear marker) were detected by Western blot analysis. (D) Following treatment for 2 h with the indicated CGP concentrations, HeLa cytoplasmic extracts (CE) were prepared and the levels of HuR and loading controls α-Tubulin and β-Actin were monitored by Western blot analysis. (E) After treatment with CGP (2 h, 10 μM), CE (10 μg) and NE (5 μg) were prepared and the levels of HuR, the cytoplasmic marker α-Tubulin, and the nuclear marker hnRNP C1/C2 were assessed by Western blot analysis. (F) Immunofluorescence microscopy to assess HuR distribution (green) in cells that were either left untreated (Unt.) or were treated with CGP (2 μM for 2 h). Nuclei were visualized using Topro-3 (blue) and the transcription factor SP1 (red). (Merged) Overlay of Topro-3, HuR, and SP1 signals. (G–I) Cells were transfected with control siRNAs (Ctrl.) or with siRNAs targeting Cdk1, Cdk7 or cyclin B1; 48 h after transfection, the levels of HuR, Cdk1, Cdk7, Cyclin B1, and loading controls β-Actin and α-Tubulin in whole-cell extracts (WE, 5 μg) and CE were monitored by Western blot analysis. Shown are fold changes in HuR levels as measured by densitometry (±SD, standard deviation from at least three experiments).