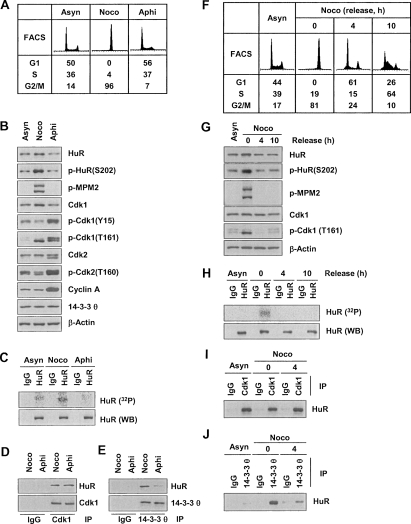
Figure 5.
Specific HuR phosphorylation and binding to 14–3–3 during G2/M. (A) FACS analysis of HeLa cells that were either growing asynchronously (Asyn) or synchronized in G2/M using nocodazole (Noco, 100 ng/mL, 16 h) or in G1 and S using aphidicolin (Aphi, 2 μg/mL, 16 h). (B) WE lysates were prepared from the populations in A, and the levels of proteins and phosphoproteins (including G1 and S markers p-cdk1 [Y15], p-cdk2 [T160], and cyclin A; G2/M marker p-cdk1 [T161], and mitotic marker p-MPM2) were assessed by Western blot analysis. (C) In vivo HuR phosphorylation was studied by incubating the populations described in A for 2 h with 32Pi and assessing the incorporation of the radiolabel into HuR by IP using anti-HuR antibody (or IgG in control IP reactions). Total HuR in IP materials was detected by Western blot analysis (WB). Co-IP analysis was used to study the association of HuR with Cdk1 (D) and with 14–3–3θ (E). (F) FACS analysis of HeLa cells synchronized with nocodazole (100 ng/mL for 16 h), released by removing nocodazole, and examined 4 and 10 h later. (G) Using cells that were processed as explained in F, the levels of the proteins shown were studied by Western blot analysis of WE lysates. (H) In vivo HuR phosphorylation was studied by incubating the populations described in F for 2 h with 32Pi and assessing the incorporation of the radiolabel into HuR by IP using anti-HuR antibody (or IgG in control IP reactions). Total HuR in IP materials was detected by Western blotting (WB). WE lysates from the populations in F were used in co-IP assays to study the association of HuR with Cdk1 (I) and with 14–3–3θ (J).