Figure 1.
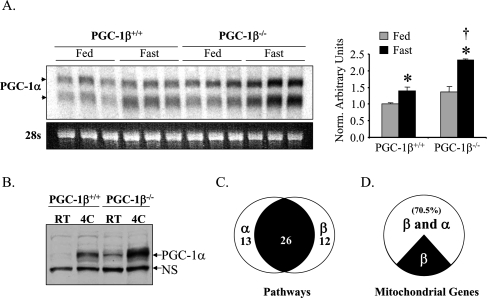
PGC-1α and PGC-1β drive a significant subset of overlapping gene regulatory programs. (A, left) Representative autoradiograph of a Northern blot using RNA isolated from heart of PGC-1β+/+ and PGC-1β−/− mice on standard chow (Fed) or post 36 h fast (Fast) is shown using a full-length PGC-1α cDNA as a probe. PGC-1α transcripts are denoted by the arrows. Ethidium bromide staining of 28s ribosomal RNA is shown at the bottom as a loading control. (Right) Quantitative RT–PCR (TaqMan) of total RNA from heart was used to characterize the level of PGC-1α gene expression in fed (gray bar) and fasted (black bars) PGC-1β+/+ and PGC-1β−/− hearts. The mRNA levels were normalized to 36Β4 mRNA content, and are shown relative to the PGC-1β+/+ fed values (=1.0). (*) P < 0.05 compared with the fed group of the same genotype; (†) P < 0.05 compared with the fasted group of the PGC-1β+/+. (B) Western blot analysis of whole-cellprotein extracts preparedfromBAT of PGC-1β+/+ and PGC-1β−/− mice at room temperature or at 4°C. The top arrow designates the full-length PGC-1α protein. A nonspecific band (NS) is shown as a loading control. (C–D) NRCM in culture were infected with Ad-GFP, Ad-PGC-1α, or Ad-PGC-1β, and gene expression array analysis was performed using the Affymetrix Rat Expression Set 230 chip. (C) Venn diagram showing the Gene Ontology pathways that were up-regulated by either PGC-1α or PGC-1β compared with Ad-GFP-infected cells. The left circle represents the pathways up-regulated by PGC-1α, and right circle represents those up-regulated by PGC-1β with overlapping portion (black) representing pathways up-regulated by both. (D) The pie chart represents genes in the Gene Ontology category “mitochondrion” that were up-regulated at least 1.5-fold by PGC-1β compared with Ad-GFP-infected cells (P < 0.05). The white portion represents those that were also up-regulated by PGC-1α by at least 1.5-fold (P < 0.05).