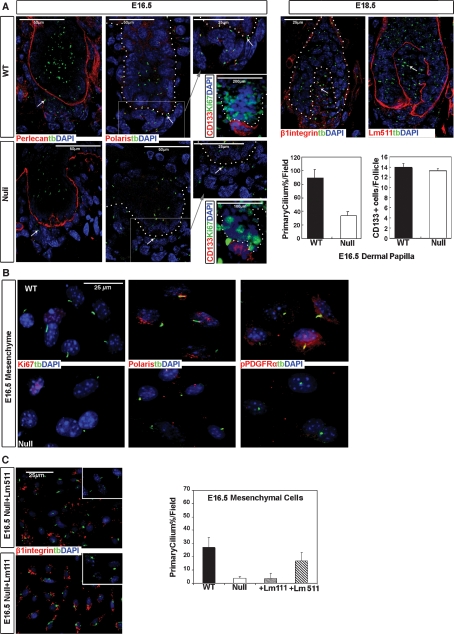
Figure 6.
Laminin-511 promotes primary cilia formation in the DP of E16.5 skin and in dermal mesenchymal cells in vitro. (A) Expression of primary cilium structural proteins (acetylated α-tubulin and polaris), basement membrane proteins, perlecan and laminin-511 (Lm511), DP marker CD133, and proliferation marker Ki67 as analyzed by immunofluorescent microscopy at E16.5 and E18.5 time points. The names and corresponding colors of antibodies in combination with blue nuclear stain (DAPI) are indicated on the panels. At the right, the total number of primary cilium in both wild-type (WT) and lama5−/− (null), and the total number of CD133-positive cells per wild type and lama5−/− DP are quantified. (B) Fresh isolated E16.5 lama5−/− (null) and wild-type (WT) primary mouse mesenchymal cells after 12 h of culture were stained with antibodies (names and corresponding colors indicated on the panels) including acytylated tubulin (tb), Ki67, polaris and PDGFRα, and phospho-PDGFRαY754 and nuclear stain (DAPI, blue) and analyzed by IF microscopy. (C) Fresh isolated E16.5 null and wild-type primary mesenchymal cells were cultured with either laminin-511 or laminin-111 for 12 h, then stained with acetylated tubulin (tb) and β1 integrin antibodies. Insets show higher magnification of primary cilia structures. The table on the right shows quantification of primary cilia formation under the different indicated conditions.