Fig. 3.
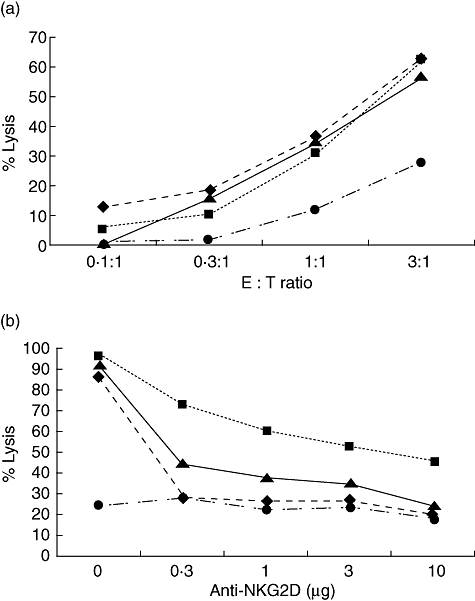
Anti-NKG2D could inhibit MICB*014-Asp136 less efficiently in NKG2D-mediated lysis. (a) Major histocompatibility complex class I chain-related gene B (MICB) transfected cells were cultured with natural killer (NK) cells. Both MICB*014 wild-type and mutants could induce NK cells to kill target cells. (b) MICB transfected C1R cells were cultured with NK cells treated with different concentrations of anti-NKG2D at an effector : target ratio of 3 : 1. Although MICB*014 (▴), MICB*014-Lys80 (♦) and MICB*014-Asp136 (▪) could induce NK cells to kill target cells compared with untransfected cells (•), MICB*014-Asp136 needed a high concentration of anti-NKG2D to block the activity of NK cells.
