Fig. 1.
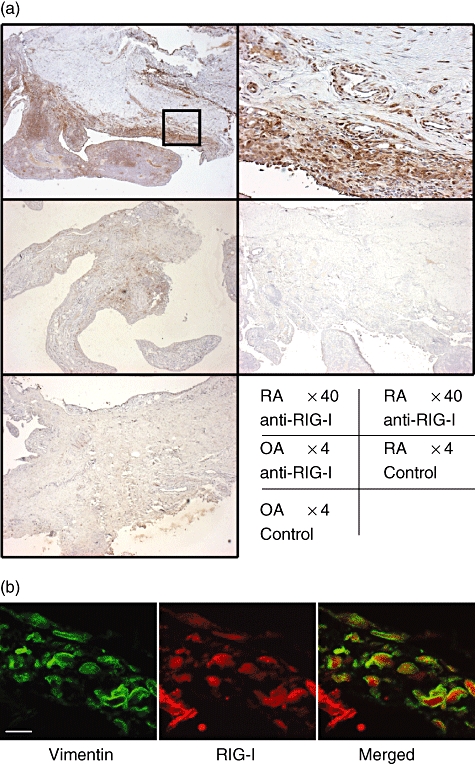
Immunohistochemical identification of retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I) in human synovial tissues. (a) Tissues obtained from patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or osteoarthritis (OA) were subjected to immunostaining using an anti-RIG-I antibody or non-immune rabbit immunoglobulin G (control). Intense RIG-I immunoreactivity was detected in synovial tissues from RA patients but not in tissues from OA patients. Upper right panel shows high power view of the square in upper left panel. The data shown are representative of three experiments. (b) Confocal microscopic images of double immunofluorescence staining for vimentin (left panel; green) and RIG-I (middle panel; red). The overlapping image was shown in right panel. Scale bar shows 10 μm.
