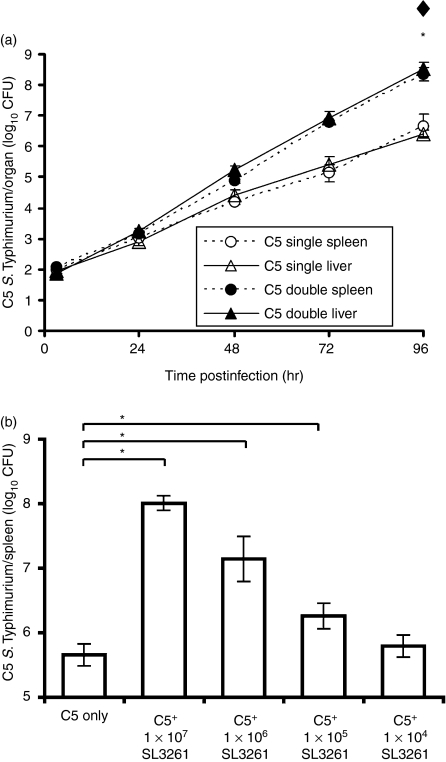
Figure 1.
Exacerbation of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium C5 viable counts caused by coadministration of S. enterica serovar Typhimurium SL3261. (a) Wild-type (WT) BALB/c mice were infected intravenously (i.v.) with 103 colony-forming units (CFU) of virulent C5 (single infections, ○ and Δ). Another group of wild-type BALB/c mice was infected i.v. with 103 CFU virulent C5 together with 1 × 106 CFU S. enterica serovar Typhimurium SL3261 (double infections, • and ▴). Spleen (circles, dotted lines) and liver (triangles, solid lines) counts of viable bacteria were obtained at times thereafter by plating organ homogenates on selective media (see Materials and methods). The results are expressed as mean log10 CFU ± standard deviation from groups of three mice per point. Rates of C5 growth in C5 single and C5 double infections were compared by linear regression analysis. *Significance at P < 0·05 for difference in rates of C5 growth in the spleen. ♦Significance at P < 0·05 for differences in rates of C5 growth in the liver. (b) Groups of five wild-type C57BL/6 mice were infected i.v. with 103 CFU of virulent C5 (C5 only), or with the same dose of C5 together with 107, 106, 105 or 104 CFU of SL3261. Three days later, viable bacterial counts in livers and spleens were assayed. For brevity, viable counts for spleen are shown but equivalent results were observed in the liver. The results are expressed as mean log10 CFU ± standard deviation. *P < 0·05 when comparing the double infected groups to the single C5-only group.