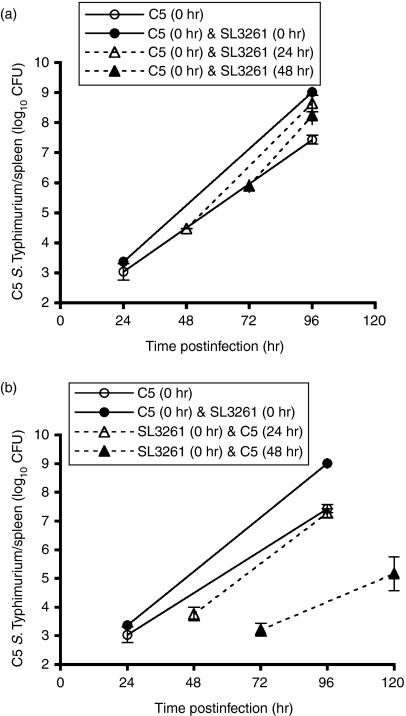
Figure 2.
Salmonella Typhimurium SL3261 can cause acceleration in the C5 growth rate even if not administered simultaneously. (a) Wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 mice were infected intravenously (i.v.) with 103 colony-forming units (CFU) of virulent C5 at time 0 (○). Three further groups of wild-type C57BL/6 mice were all given 103 CFU of virulent C5 at time 0 and then given 106 CFU SL3261 at 0 hr (•), 24 hr (▴) or 48 hr (▴). Viable bacterial counts were obtained from spleens 24 hr after SL3261 infection and then at 96 hr. Mice in the C5-only group were assayed for viable bacterial counts at 24 and 96 hr postinfection. The results are expressed as mean log10 CFU ± standard deviation for four mice per point. (b) Wild-type C57BL/6 mice were infected i.v. with 103 CFU of virulent C5 at time 0 (○). Three further groups of wild-type C57BL/6 mice were given 106 CFU of SL3261 at time 0 and then given 103 CFU of C5 at 0 hr (•), 24 hr (▴) or 48 hr (▴). Viable bacterial counts were obtained from the spleen at 24 hr after C5 infection and then at 96 or 120 hr. The C5-only group was assayed for viable bacterial counts at 24 and 96 hr postinfection. The results are expressed as mean log10 CFU ± standard deviation of four mice per point. For brevity, viable counts for spleen are shown but equivalent results were observed in the liver.