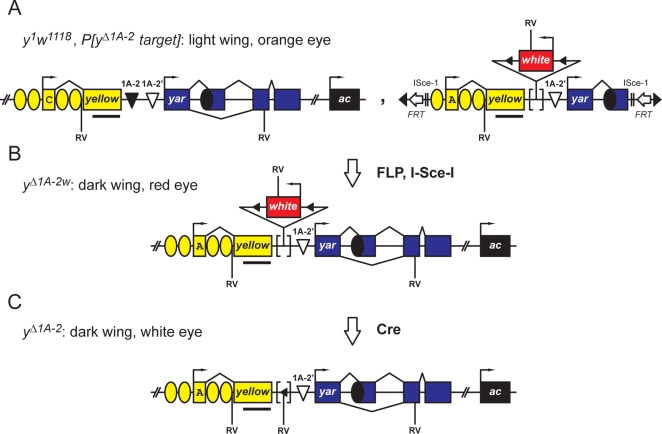
Figure 5. Ends-out targeting strategy to generate deletions of 1A-2 at the endogenous 1A locus.
A. Transgenic flies were generated that carried the mutant y1 allele (structure shown where C indicates the mutation of the translation ATG start) at the endogenous X chromosome location (left) and the P[yΔ1A-2 target] transposon on a different chromosome (right) that carries a y gene lacking the wing enhancer, but encodes a wild type RNA (A indicates the presence of the correct translation ATG start). In this transposon, the y gene, flanked by FRT sites (white arrows) and I-SceI sites, is within a P transposon (inverted black triangles). Other symbols representing the y, yar and ac genes are as described in Figure 1. Transgenic flies y1 w1118, P[yΔ1A-2 target] had a light wing color and orange eyes. B. FLP and I-SceI enzymes catalyzed replacement of the y1 allele at the endogenous locus, with yΔ1A-2w, in which the 1A-2 insulator is substituted by the whs gene (raised triangle) inserted between loxP sites (black arrowheads on raised triangle). The recombinant yΔ1A-2w flies had dark wings and red eyes. C. Cre recombinase deleted the whs gene, leaving behind a single loxP site to form yΔ1A-2. In the case of the yΔ1A-2, the remaining loxP site was mutated, forming a new EcoRV site (RV), whereas in the similarly derived yΔ1A-2/Δ1-A2′ flies a wild type loxP site remained. The bar under the y gene indicates the probe used in the Southern analyses (see Figure S1).