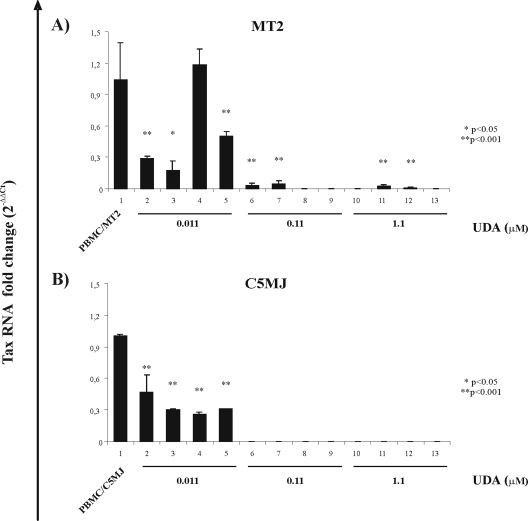
FIG. 2.
Effects of UDA on HTLV-1 tax RNA expression evaluated in real-time PCR 4 weeks after in vitro PBMC exposure to irrMT-2 cells (A) or irrC5MJ cells (B). (A) Bar 1, PBMC/MT-2, infected, untreated control; bar 2, PBMCpt, PBMCs pretreated with 0.011 UDA; bar 3, MT-2pt, MT-2 pretreated with 0.011 UDA; bar 4, PBMCpt/MT-2pt, both PBMCs and MT-2 cell lines singly pretreated with 0.011 UDA; bar 5, PBMC/MT-cot, UDA at concentrations indicated above was added at the time of cocultivation and exposed to irrMT-2 cells. For bars 6, 7, 8, and 9, conditions were as indicated above but in the presence of 0.11 μM UDA. For bars 10, 11, 12, and 13, conditions were as above but in the presence of 1.1 μM UDA. The error bars indicate standard errors. (B) For C5MJ cells, the same culture conditions were applied: bar 1, PBMC/C5MJ, infected untreated control; bar 2, PBMCpt, PBMCs pretreated with 0.011 UDA; bar 3, C5MJpt, C5MJ pretreated with 0.011 UDA; bar 4, PBMCpt/C5MJpt, both PBMCs and C5MJ cell lines singly pretreated with 0.011 UDA; bar 5, PBMC/C5MJcot, UDA at concentrations as indicated above was added at the time of cocultivation and exposed to irradiated C5MJ cells. For bars 6, 7, 8, and 9, conditions were as indicated above but in the presence of 0.11 μM UDA. For bars 10, 11, 12, and 13, conditions were as above but in the presence of 1.1 μM UDA. *, P value significant, P < 0.05; **, P value highly significant, P < 0.001.