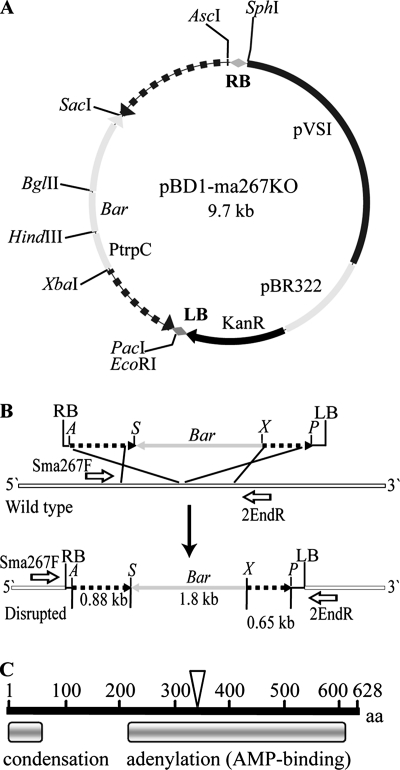
FIG. 1.
Strategy for targeted disruption of MaNPS1. (A) Binary vector pBD1-ma267KO, which encodes the Bar gene conferring resistance to GA whose expression is driven by the TrpC promoter (PtrpC) of Aspergillus nidulans. Hashed lines on either side of the PtrpC-Bar gene are the flanking regions of clone Ma#267 of MaNPS1. (B) Schematic of a homologous recombination event between the Ma#267 gene disruption construct and the wild-type MaNPS1 gene, which results in the insertion of a functional copy of the Bar gene into the MaNPS1 gene. Sma267F and 2EndR are forward and reverse primers, respectively, that hybridize to wild-type MaNPS1 DNA flanking the insertion point of the disruption construct. These primers were used to screen Bar-resistant transformants for a targeted gene disruption event. (C) Schematic of the conserved domains of the predicted protein of clone Ma#267 of MaNPS1, which contains part of a condensation domain and a full-length adenylation domain of an elongation module. The inverted triangle represents the approximate site at which the MaNPS1 gene was disrupted with the Bar gene.