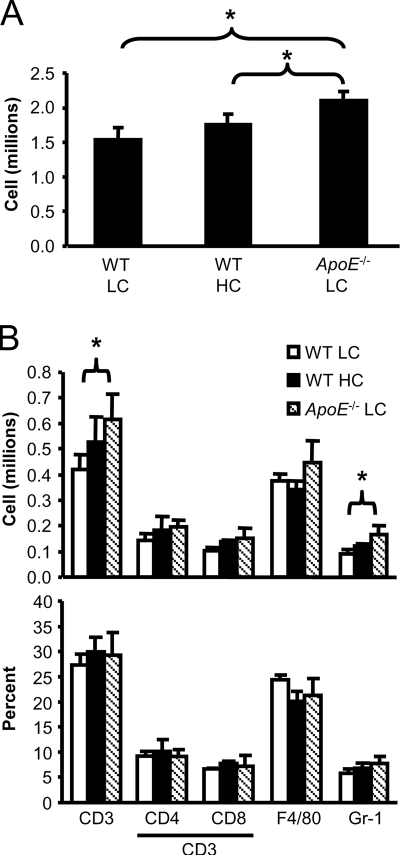
FIG. 3.
Lung inflammation increases with increasing serum cholesterol. (A) Lung leukocyte counts for the right caudal and left lung lobes of WT LC, WT HC, and ApoE−/− LC mice 12 weeks after aerosol infection with M. tuberculosis. The values are the mean numbers of cells expressed in millions plus standard deviations (SD). *, P < 0.05 (n = 5). (B) The total numbers (top graphs) and percentages (bottom graphs) of T cells (CD3+ CD4+/CD8+), macrophages (F4/80+), or granulocytes (Gr-1+ CD3− F4/80−) isolated from the right caudal and left lung lobes of WT LC, WT HC, and ApoE−/− LC mice 12 weeks after aerosol infection with M. tuberculosis. The total number of each cell population was determined by multiplying the percentage of cells positive for the above-mentioned surface markers by the total number of lung leukocytes isolated from each mouse. The values are the mean numbers of cells expressed in millions plus SD. *, P < 0.05 (n = 4). The results shown are representative of one experiment.