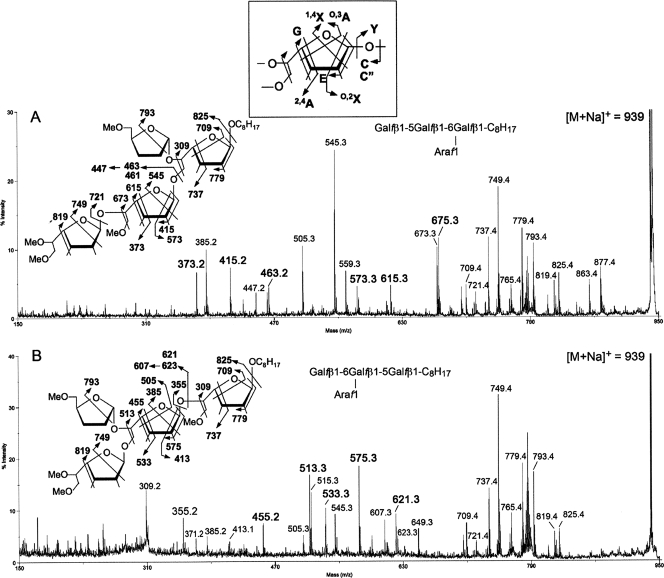
FIG. 7.
MALDI-TOF/TOF MS/MS analysis. Shown are the enzymatic product Gal3Ara1-C8H17 obtained from using the synthetic acceptor β-d-Galf-(1→5)-β-d-Galf-(1→6)-β-d-Galf-octyl (A) and β-d-Galf-(1→6)-β-d-Galf-(1→5)-β-d-Galf-octyl (B). The [M + Na]+ molecular ions afforded by the permethylated sample at m/z 939 (Fig. 6) were selected for high-energy CID MS/MS. Assignment of the key fragment ions were as schematically illustrated. In addition to the well-established A, X, C, and Y ions, the G and E ions were named by Spina et al. and have been described in full in the context of furanoses (18, 32). (Note that the 1,4X ions give linkage information only pertaining to the C-1 position. The 0,2X ions provide information about whether C-2 contains a glycosidic bond. 0,3A and 2,4A ions provide the C-5 and C-3 linkage information. C and Y ions, as well as the E and G ions, represent concerted elimination of substituents around the ring.) The two specific ion series corresponding to E − 30 mass units and C − 16 mass units (m/z 447 and 607, respectively) were likewise identified previously for the arabinan and not further drawn out here. The concerted cleavages corresponding to loss of both C-5 and C-6 substituents on the Galf have not been reported before and were noted to produce a pair of ions differing in having either unsaturated or saturated bonds (e.g., m/z 675/673 in panel A and 513/515 in panel B). The 1,4X ions at m/z 385 in panel A and 545 in panel B coincide, respectively, with the E ions at m/z 415 and 575 − 30 mass units and thus may not be taken as sequence-specific ions to indicate presence of isomeric products. In contrast, other specific ions as described in the text are present only in either and not both spectra. The ion at m/z 505 in panel A may be assigned as an O,3A ion, which is indicative of possible presence of Araf on the nonreducing terminal Gal2, as in panel B, but other supporting ions that are specific to this isomeric structure are lacking.