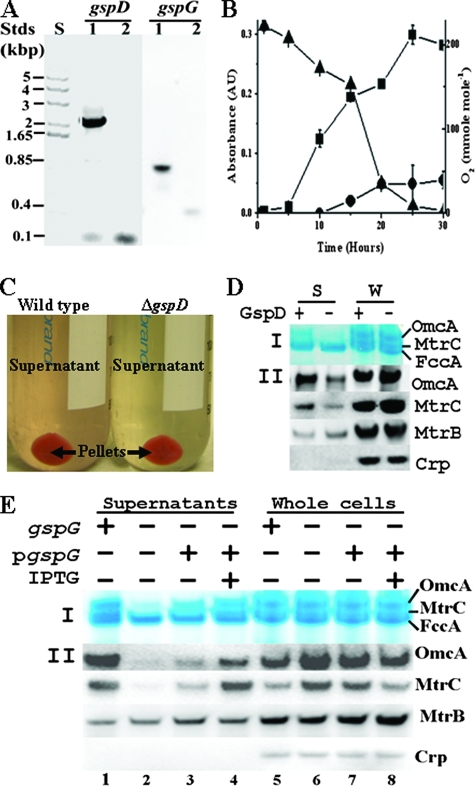
FIG. 1.
Influence of deletion of gspD or gspG on extracellular release of native MtrC and OmcA. (A) Agarose gel showing size of DNA standards (Stds) in kilobase pairs (lane S) and PCR products of the gspD or gspG amplified from the wt (lanes 1) and the respective mutants (lanes 2). (B) Bacterial culture of wt. The optical density at 600 nm of cell culture (▪), the optical density at 525 nm of the filtrate of cell culture (•), and the O2 concentration (▴) in the headspace of serum bottle during the time course of the study were measured. For points without an error bar, the error was smaller than the symbol (n = 3). (C) Colors of the supernatants of wt and ΔgspD cultures under O2-limited growth condition. (D and E) Heme staining and Western blot analyses of the effects of deleting gspD (D) or gspG (E). After 2 μg of concentrated supernatant proteins (lanes S [D] and lanes 1 to 4 [E]) or 10 μg (D) or 5 μg (E) of whole-cell lysate proteins (lanes W [D] and lanes 5 to 8 [E]) from wt (lanes +) and respective mutant (lanes -) were separated by SDS-PAGE, they were either visualized by heme staining (I panel) or probed with the respective antibodies (II panels).