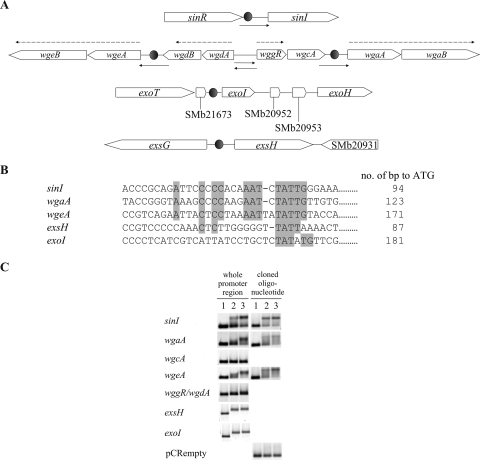
FIG. 2.
(A) The galactoglucan biosynthesis gene region from wgaA to wgeB (expE2) (10,330 bp) from the galactoglucan biosynthesis gene cluster of S. meliloti (16). Promoter regions used for gel shift assays and determination of expression levels are indicated by solid arrows. ExpR binding sites are indicated by filled circles. Transcriptional units are marked by broken arrows. (B) ExpR binding-site consensus. The identified ExpR binding sites from the promoter regions of sinI, wgaA, and wgeA were aligned in the 5′-to-3′ orientation to show homology. Sequences from the promoter regions of exsH and exoI exhibiting weak homology to the consensus are included. (C) AHL-enhanced DNA binding of purified His6-ExpR to the galactoglucan biosynthesis gene promoter regions. (Left) Cy3-labeled promoter regions of wgaA, wgeA, and wgdA and/or wggR were used in the gel shift assay. (Right) Oligonucleotides (indicated by the dark gray boxes in Fig. 3) covering the ExpR binding sites within the sinI, wgaA, and wgeA promoters cloned into vector pCR. DNA fragments from the pCR-oligonucleotide constructs were amplified and Cy3 labeled and are included in the gel shift assays, along with a Cy3-labeled fragment from the empty vector as a negative control. For each panel, lane 1 is the Cy3-labeled DNA only, lane 2 is Cy3-labeled DNA mixed with His6-ExpR, and lane 3 is a mixture of Cy3-labeled DNA, His6-ExpR, and oxo-C14-HL.