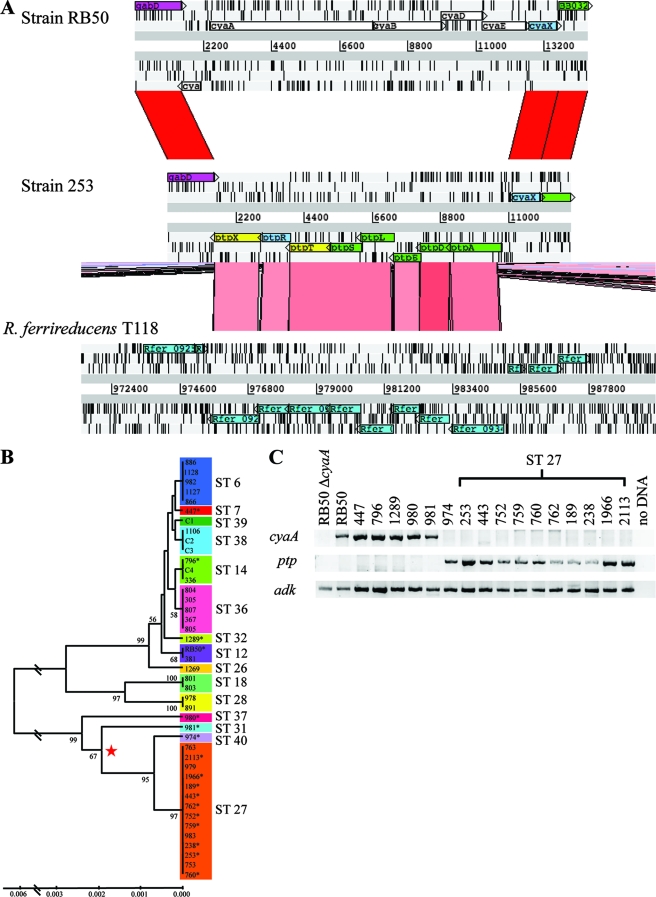
FIG. 4.
Loss of cyaA is shared among a B. bronchiseptica lineage. (A) Artemis Comparison Tool snapshot of BLASTN comparison between strain RB50 (top) and 253 (middle) and TBLASTX comparison of strain 253 (middle) and R. ferrireducens (bottom) genomes. Areas of sequence similarity are indicated by red bands (99% identity) and pink bands (45 to 64% identity). Arrows indicate the direction of transcription. Each gene is labeled as annotated in the RB50, 253, and R. ferrireducens T118 genomes. (B) A UPGMA tree with 1,000 bootstraps based on the concatenated MLST gene sequence of 43 B. bronchiseptica isolates. The colors correspond to the indicated STs. The numbers on the tree branches indicate the branch strength. All branch strengths below 50 were removed. The identification number of each strain is listed. The asterisks next to the strain numbers in panel B indicate the isolates examined in panel C. The red star in indicates the emergence of a B. bronchiseptica lineage lacking cyaA and containing the ptp genes. (C) PCR amplification of cyaA, the novel sequence predicted to encode peptide transport proteins present in 253 and adk in six non-ST27 strains, one ST40 strain, 10 ST27 strains, and RB50ΔcyaA. A sample containing no DNA template was included to ensure the absence of DNA contamination.