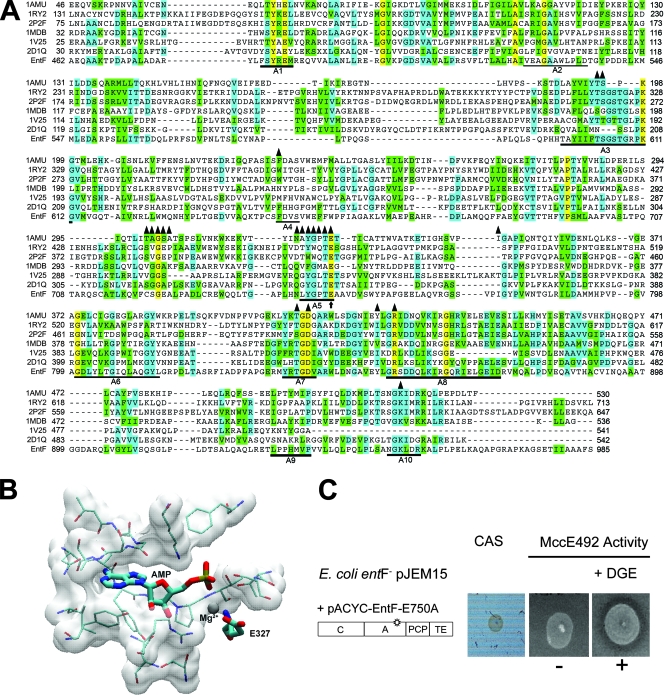
FIG. 3.
Design of the E750A mutation in the EntF A domain and its effect on MccE492 maturation. (A) Alignment of the relevant region of the EntF A domain with the sequences of different crystallized adenylation domains obtained from the following PDB files: 1AMU, 1RY2, 2P2F, 1MDB, 1V25, and 2D1Q. Residues in yellow are 100% conserved. Residues in green and blue are conserved substitutions according to Vector NTI nomenclature (green, conserved substitutions with respect to the consensus; blue, identical residues with respect to the consensus). Triangles mark the residues located 5 Å or less from the active site in the 1AMU crystal structure. The arrow marks the residue selected for mutagenesis. (B) Structure of the active site of the 1AMU protein with bound AMP-Mg. Mg2+ and AMP are shown in the structure. The selected residue (E327) is equivalent to residue E750 in EntF. (C) The EntF E750A mutant was evaluated for the ability to produce enterochelin (CAS plate) and active MccE492 in a sensitive lawn supplemented with DGE. The host used was E. coli ER1300H (entF)/pJEM15, and E. coli BL21(DE3) was used as the indicator strain.