Figure 2. Model of FKBP51, FKBP52 and PP5 regulation of GR function.
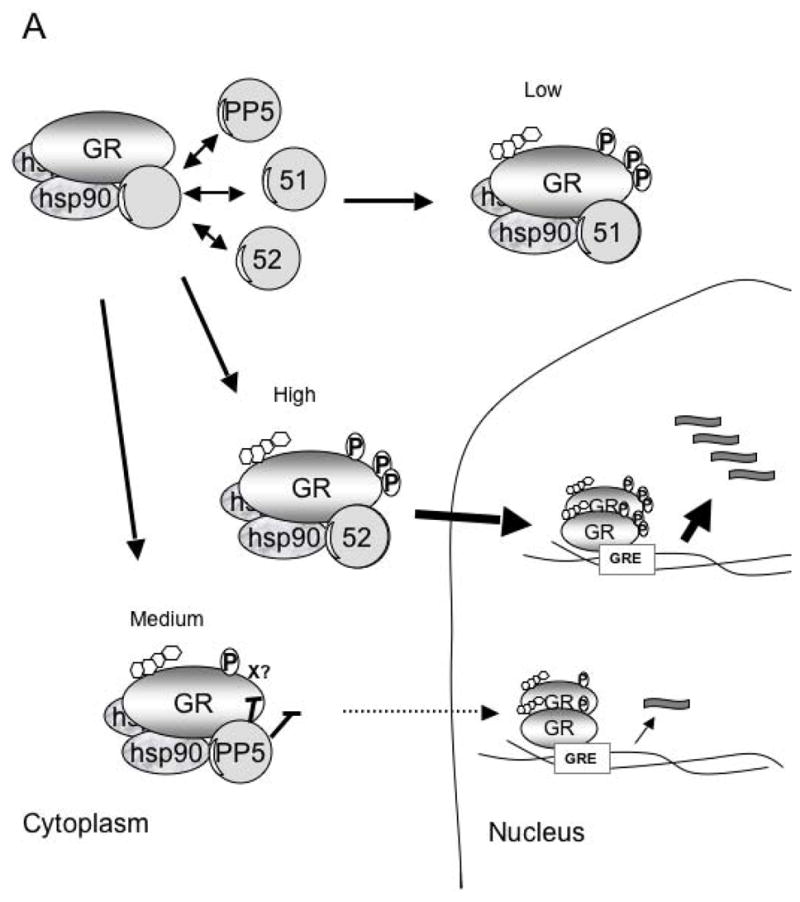
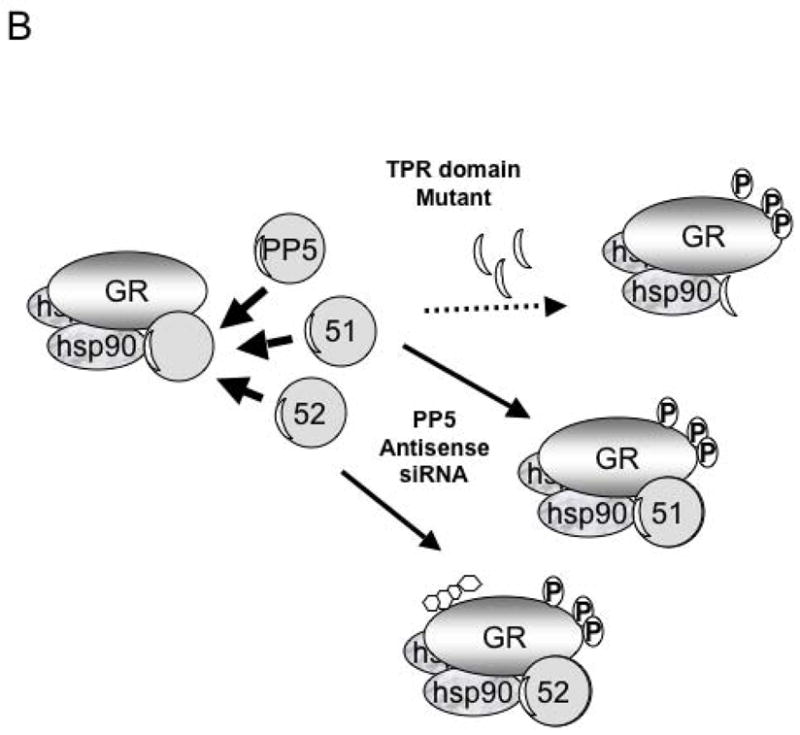
A) The GR-heterocomplex can contain FKBP51, FKBP52 or PP5. In the basal state the inactive GR-heterocomplex contains FKBP51 as the predominant TPR protein. In this state GR has low hormone binding activity. The acquisition of PP5 by the GR-complex results in a GR-with intermediate hormone-binding and transcriptional activities. When the GR acquires FKBP52, it has the highest transcription activity due to both enhanced hormone binding affinity and enhanced nuclear translocation. B) The model above enlightens previous conflicting experiments such that the over expression of the TPR-domain (thought to be a dominant-negative mutant) of PP5 prevents the binding of FKBP52, favoring the cytoplasmic retention of the GR-complex in a state with low affinity for hormone. The suppression of PP5 expression has the opposite effect, facilitating FKBP52-GR interactions, which favors hormone binding, increased nuclear translocation and enhanced transcriptional activity.
