Figure 3. Roles of PP5 in the regulation of stress-induced signaling cascades.
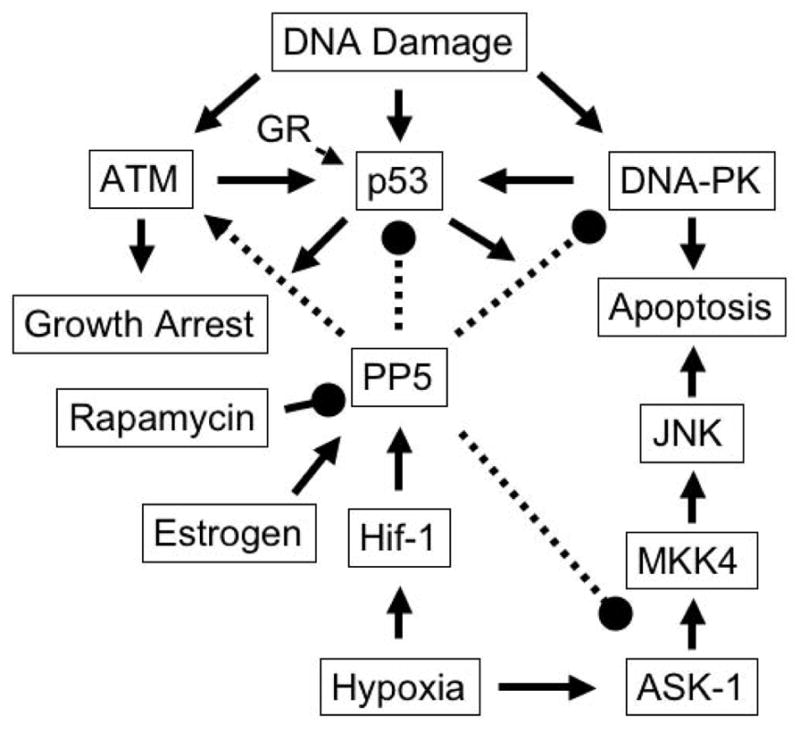
In response to DNA damage, ATM, p53 and DNA-PK are activated, triggering and/or propagating signaling cascades leading to growth arrest or apoptosis. Both hypoxia and 17-β estradiol induce PP5 transcription, leading to the suppression of p53-, DNA-PK- and ASK-1-mediated responses that result in growth arrest or apoptosis. In p53 −/− cells rapamycin produces a decrease in PP5 activity and a concomitant increase in ASK-1 mediated apoptosis suggesting that the suppression of PP5 activity contributes to the antitumor activity of rapamycin. PP5 has also been reported to play a positive role in the propagation of an ATM-mediated response leading to growth arrest. Arrows indicate stimulatory actions. Lines with filled circles at the end indicate inhibitory actions.
