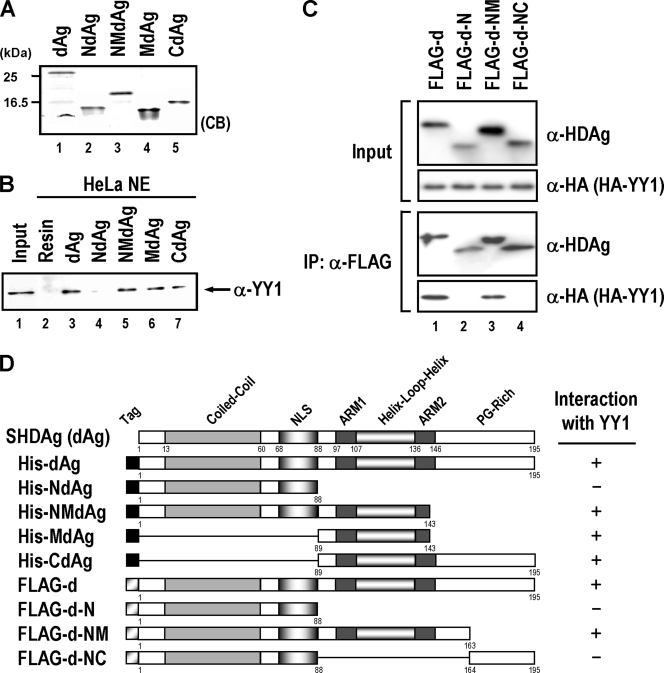
FIG. 2.
Mapping of the YY1-interacting region in HDAg. (A) Partial purified His-tagged SHDAg (dAg) and its various derivatives NdAg, NMdAg, MdAg, and CdAg (1 μg each) were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected by Coomassie brilliant blue (CB) staining. (B) In vitro binding assay of His-tagged SHDAg variants and cellular YY1. The nuclear extracts (NE) of HeLa cells (200 μg) were incubated with 20 μl of His-resins (lane 2) or His resins prebound with SHDAg derivatives (lanes 3 to 7) as indicated, and proteins bound on the beads were eluted and analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with anti-YY1 antibody. Input: 50 μg of HeLa nuclear extracts (lane 1). (C) Further mapping of YY1 interaction domain on SHDAg. Expression plasmids of FLAG-tagged SHDAg (FLAG-D) or its derived truncated mutants (FLAG-d-N, FLAG-d-NM, and FLAG-d-NC) were used to transfect with the expression plasmid of HA-tagged YY1 to HuH-7 cells. Transfected cells were harvested at 2 days posttransfection and then analyzed by a coimmunoprecipitation assay. For the coimmunoprecipitation, the extracts from the transfected cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG M2 affinity gel (10 μl, packed volume; Kodak) in the presence of RNase A (10 μg/ml) and incubated at 4°C for 1 h with agitation. The immunoprecipitates were washed four times with PBS buffer containing 0.3% NP-40 and processed for Western blotting (rabbit anti-HA antiserum for HA-tagged YY1 and rabbit anti-FLAG antiserum for FLAG-tagged SHDAg and its truncation mutants). (D) A schematic diagram showing the interaction region of YY1 within SHDAg. The numbers represent the positions of the amino acid residues of SHDAg and its variants. The interaction ability of SHDAg and its variants with YY1 is indicated by a plus or a minus sign. NLS, nuclear localization signal; PG-rich: proline/glycine-rich; α, anti; IP, immunoprecipitation.