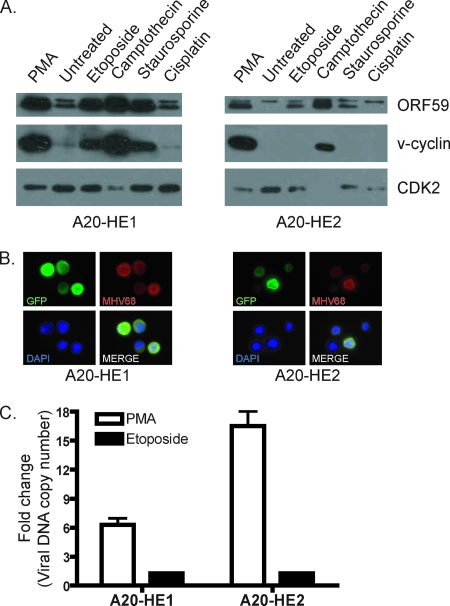
FIG. 6.
Induction of lytic antigens by DNA damage stimuli. (A) A20-HE cells (5 × 105 per ml) were treated with etoposide (25 μM), camptothecin (2 μM), staurosporine (20 μg/ml), or cisplatin (100 μM). PMA (20 ng/ml) and untreated cells served as respective positive and negative controls. Cells were harvested 24 h posttreatment. Total protein (50 μg) was resolved by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblot analysis for the indicated viral or cellular (CDK2) antigens. (B) A20-HE cells were treated with 50 μM etoposide and processed for immunofluorescence microscopy 24 h posttreatment. Cells were stained with antibodies to GFP and MHV68 antisera. DNA was detected with DAPI in the mounting media. Magnification, ×100. (C) Total DNA (200 ng) was analyzed by quantitative PCR for the presence of viral genome using orf50-specific primers. Data represent the fold increase following 24 h of stimulation with PMA (20 ng/ml) or etoposide (25 μM) relative to vehicle-treated controls. Results are means of triplicate samples. Error bars represent standard deviations.