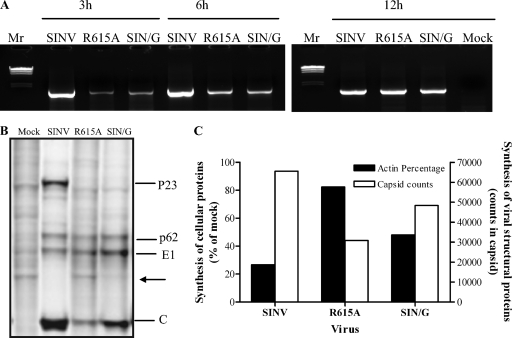
FIG. 7.
Comparison of phenotypic characteristics for R615A and SIN/G. (A) Minus-strand RNA synthesis. BHK cells were infected with wild-type virus (SINV), R615A, or the SIN/G mutant at an MOI of 10. At different times postinfection cytoplasmic RNA was extracted and used in a minus-strand-specific two-step RT-PCR as described in Materials and Methods. (B) Comparison of virus and cellular protein synthesis in cells infected with R615A, SIN/G, or wild-type (SINV) virus. BHK-15 cells were infected at an MOI of 10 and maintained at 37°C. At 8 h postinfection proteins were pulse labeled with [35S]methionine at the indicated times and analyzed on an SDS-10% polyacrylamide gel. Gels were dried and autoradiographed. The positions of SINV structural proteins and uncleaved P23 are indicated. The position of the actin band is indicated by an arrow. (C) The synthesis of cellular proteins in infected cells was analyzed by measuring the radioactivity counts in the actin band, and the results were normalized on the amount of radioactivity detected in uninfected cells. Viral protein synthesis in infected cells was evaluated by measuring the radioactivity counts in the band of the capsid protein.