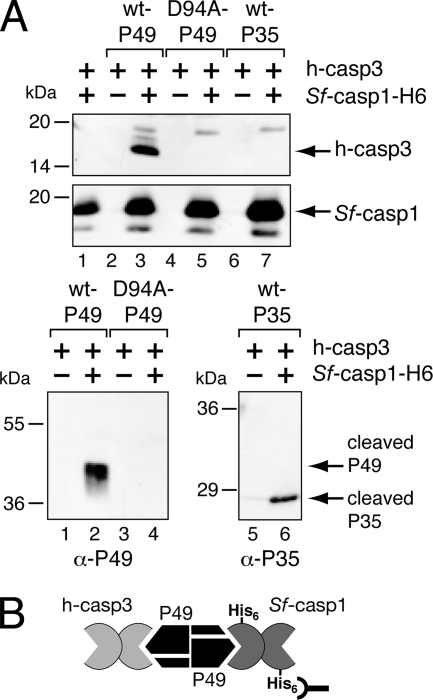
FIG. 3.
Divalent caspase interactions with P49. (A) Formation of caspase complexes. E. coli extracts containing active human caspase-3 (h-casp3) (+) were mixed with extracts of untagged wild-type (wt) P49 (lanes 2 and 3), P49D94A (lanes 4 and 5), or wild-type P35 (lanes 6 and 7) and incubated with (+) or without (−) purified active Sf-caspase-1-His6 for 1 h at 37°C. Both human caspase-3 and Sf-caspase-1 are spontaneously processed to their mature, active subunits when overproduced in E. coli. The reaction mixtures were subjected to Ni2+ affinity chromatography followed by immunoblot analysis by using large subunit-specific anti (α)-human caspase-3 (top), large subunit-specific anti-Sf-caspase-1 (middle), anti-P49 (bottom left), or anti-P35 (bottom right). Molecular mass standards are indicated to the left of each panel. (B) Model of the P49/caspase complex. By virtue of its interactions with dimeric P49, the active form of untagged human caspase-3 forms a complex with His6-tagged Sf-caspase-1 that can be isolated by Ni2+ pull-down.