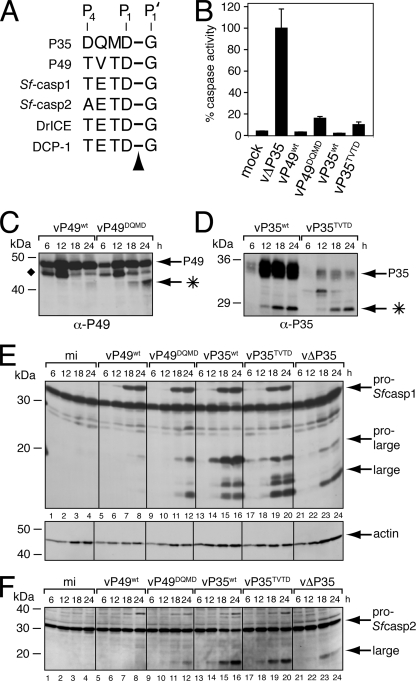
FIG. 6.
P49DQMD and P35TVTD fail to inhibit the Spodoptera initiator caspase during infection. (A) Caspase cleavage sites. The P4 to P1 caspase recognition residues of P35 and P49 are compared with those at the large/small subunit junctions of Spodoptera and Drosophila effector caspases. The arrowhead denotes the cleaved P1-P1′ peptide bond. (B) Intracellular caspase activity. Cytoplasmic extracts of SF21 cells prepared 24 h after infection with recombinant baculoviruses encoding the indicated proteins as their sole apoptotic inhibitor were assayed for caspase activity by using substrate DEVD-AMC. Plotted values are the averages ± standard deviations of samples taken from triplicate infections and are reported as percentages of the 24-h caspase activity of vΔP35-infected cells. α, anti. (C to F) Immunoblots. Total lysates of cells harvested at the indicated hours after infection with the viruses described for panel B were subjected to immunoblot analysis by using (C) anti-P49, (D) anti-P35, (E) anti-Sf-caspase-1 (top) and antiactin (bottom), or (F) anti-Sf-caspase-2. Actin levels indicate comparable protein loading. The P49 and P35 cleavage fragments (*) and the unidentified P49-related protein (⧫) are indicated. Molecular mass standards are included on the left of each panel.